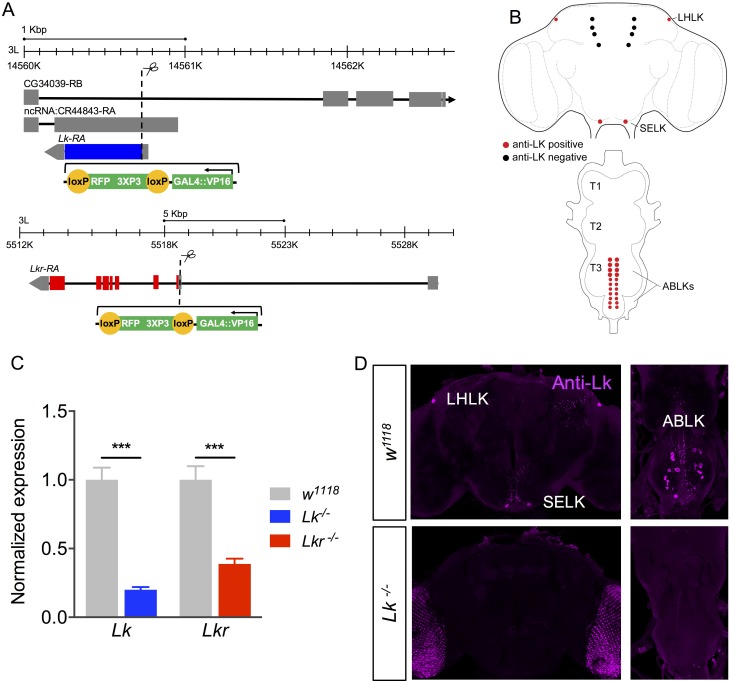
Fig 1. Generation of Lk and Lkr GAL4 knock-in mutants.
(A) Schematics of the Lk and Lkr gene loci and the locations of construct insertion to generate GAL4 knock-in mutants. Note that CG34039 and ncRNA represent predictions for the presence of coding and non-coding genes in the same chromosome and overlapping location as Lk. However, there is no evidence that they are functional. Potentially, these two genes are encoded on the sense strand while Lk is on the anti-sense strand. (B) A schematic of the adult CNS showing the location of LK-expressing neurons [based on [7,8,10]]. LHLK, lateral horn LK neuron; SELK, subesophageal ganglion LK neuron; ABLK, abdominal LK neuron, T1 –T3, thoracic neuromeres. (C) Quantitative PCR shows a significant reduction in Lk and Lkr transcripts in Lk and Lkr homozygous mutants, respectively. (*** p < 0.001 as assessed by unpaired t test). (D) LK-immunoreactivity is completely abolished in the brain and ventral nerve cord of Lk mutants.