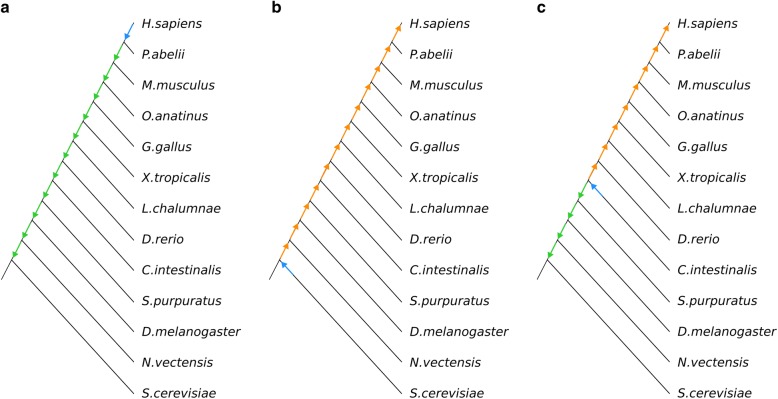
Fig. 1.
Simplification of a step-wise search strategy to locate homologs at increasingly distant taxonomic divisions from human. Assuming we want to study the evolution of a protein family from a common ancestor of human and yeast, towards a human protein member of this family, we can collect selected homologs in three ways (see text for details). From a) human to S. cerevisiae, if we start from a human protein, b) from S. cerevisiae to human, if we start from a yeast protein, and c) from an intermediate species such as C. intestinalis both to human and S. cerevisiae. The color of the arrows represents either the starting species for the search (blue), or whether the direction of the search is towards closer (orange) or further (green) taxonomic divisions to human