Fig. 5. miR-27a downregulation was critical for ChlA-F-induced stabilization of SESN2 mRNA, autophagy induction, and anchorage-independent growth inhibition in human invasive BC cells.
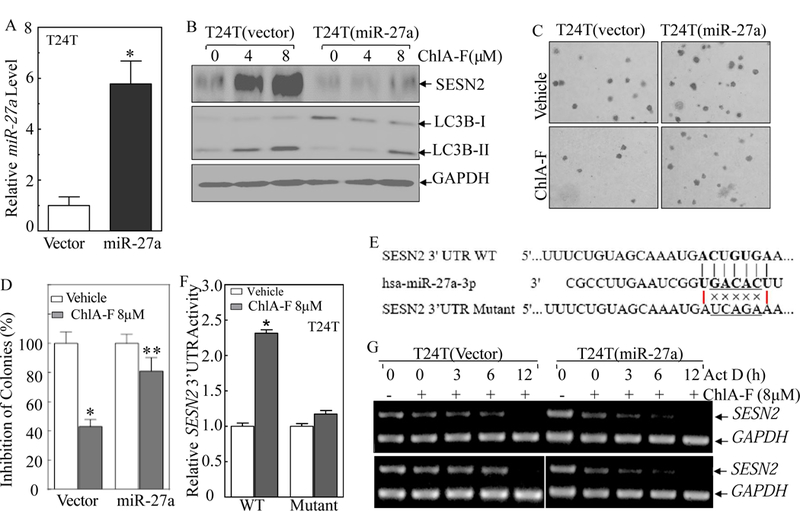
(A) Overexpression of miR-27a in T24T cells was identified by real-time PCR assay. (B) Ectopic expression of miR-27a reversed ChlA-F-induced SESN2 abundance and autophagy induction in T24T cells. (C & D) Representative images of colony formation of T24T(miR-27a) and T24T(Nonsense) cells in soft-agar assay in the presence or absence of ChlA-F (8 µM) were captured (C) and scored (D) under an inverted microscope. The results are presented as colonies per 104cells.The bars show Mean ± SD from three independent experiments. The symbol (*) indicates a significant decrease from vehicle control (p<0.05) (D). (E) Schematic of the miR-27a binding sites and its mutant of the pMIR-report-SESN2 3’UTR luciferase reporter. (F) Attenuation of ChlA-F induction of SESN2 mRNA 3’UTR activity in the miR-27a binding site mutant of pMIR-report-SESN2 3’UTR transfectants. (G) T24T cells were incubated with Act D (20 µg/ml) for the indicated time periods with or without ChlA-F (8 µM). Total RNA was isolated and RT-PCR was then performed to determine SESN2 mRNA levels. The result are representative of three independent experiments.
