Fig. 6. ChlA-F treatment impaired miR-27a maturation accompanied by specific attenuation of Dicer protein, but not mRNA expression in human invasive BC cells.
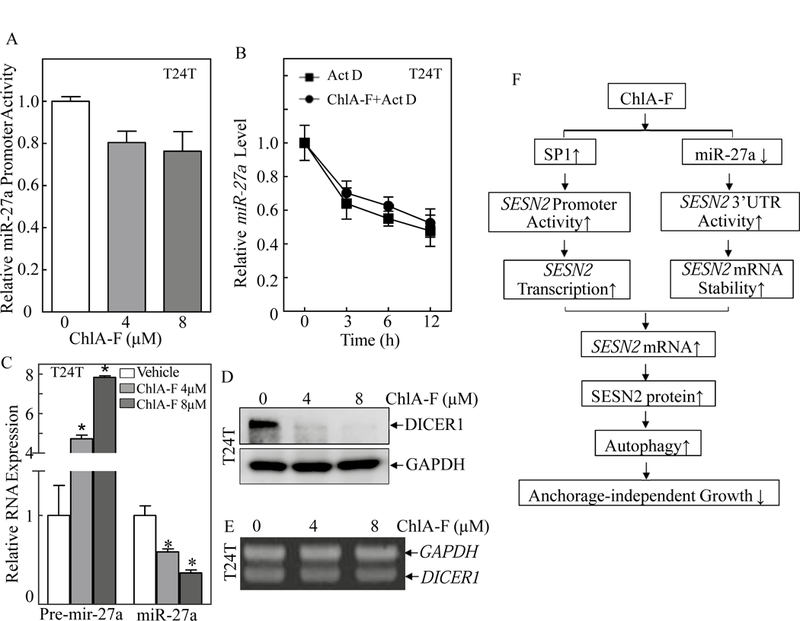
(A) T24T stably transfected with miR-27a promoter-driven luciferase reporter was treated with ChlA-F at different concentrations for 12 h to determine the potential effect of ChlA-F on miR-27a promoter transcriptional activity. (B) T24T cells were co-incubated with ChlA-F (8 µM) and Act D (20 µg/ml) for the indicated time periods. Total RNA was isolated and quantitative real-time PCR was then performed to determine miR-27a levels. The fold change was normalized to internal control gapdh. The result is representative of three independent experiments. (C) The relative expression levels of pre-mir27a and miR-27a were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR in T24T followed by ChlA-F treatment at different concentrations for 12 h. The symbol (*) indicates a significant change from vehicle control (p<0.05). (D) T24T cells were treated with various concentrations of ChlA-F for 12h. The cell lysates were subjected to Western Blot to detect Dicer protein expression. (E) Total RNA was isolated from the T24T cells treated with the indicated concentrations of ChlA-F for 12 hours. RT-PCR was performed to determine dicer mRNA levels. The gapdh mRNA levels were used as loading control. (F) The schematic summary of molecular mechanisms underlying anticancer activity of ChlA-F on human bladder cancers.
