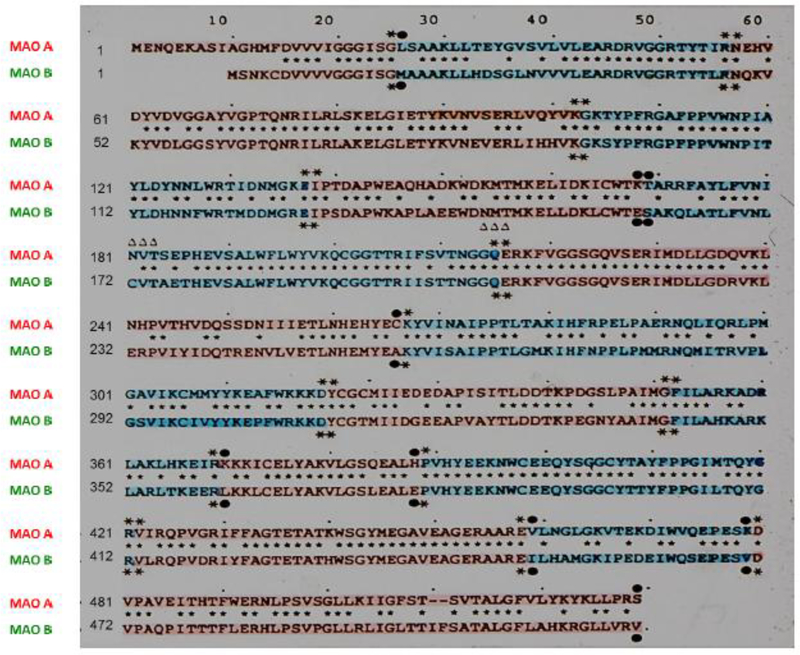
Fig. 1. The alignment of deduced polypeptide sequences shows that MAO A and B are encoded by different genes with 70% amino acid identity with identical intron-exon organizations and thus termed isoenzymes.
Amino acids are numbered on the left side. Identical amino acids are indicated by asterisks. Dashes mark spaces introduced for maximum alignment of identical residues. Pink or blue shade denotes amino acids in each exon. Identical or divergent amino acids at the 5’ or 3’ boundary of the introns are indicated by bold asterisks or filled circles, respectively. Triangles denote potential glycosylation sites. (Adapted from Bach et al., 1988; Grimsby et al., 1991)