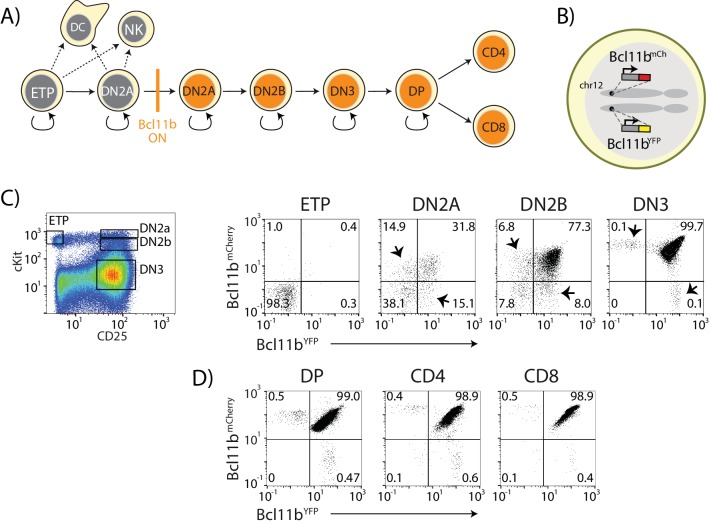
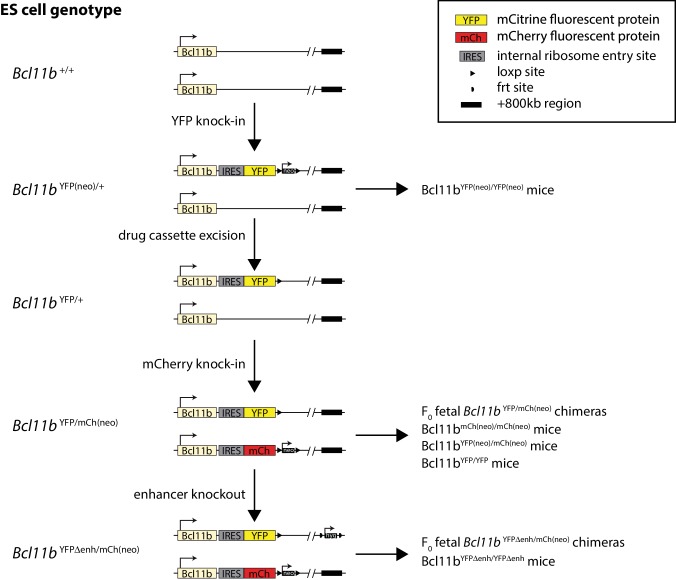
Figure 1. Dual-color Bcl11b reporter strategy can reveal epigenetic mechanisms controlling T-cell lineage commitment.
(A) Overview of early T-cell development. Bcl11b turns on to silence alternate fate potentials and drive T-cell fate commitment. ETP – early thymic progenitor; DN2 – CD4- CD8-double negative-2A progenitor; DP – CD4+ CD8+; NK – natural killer; DC – dendritic cell. (B) Dual-allelic Bcl11b reporter cells, where two distinguishable fluorescent proteins (YFP and mCherry) are inserted non-disruptively into the same sites on the two endogenous Bcl11b loci. (C) Flow cytometry plots show cKit versus CD25 levels in CD4-CD8- double negative (DN) thymic progenitors (left), along with Bcl11b-YFP versus Bcl11b-mCh expression levels in the indicated DN progenitor subsets from dual Bcl11b reporter mice. Arrowheads indicate cells expressing one copy of Bcl11b. (D) Flow plots show Bcl11b-YFP versus Bcl11b-mCh levels in CD4+CD8+double positive (DP) T-cell precursors from the thymus (left), or CD4 (center) or CD8 (right) T-cells from the spleen. Results are representative of analysis of 6–8 mice from two independent experiments. See also Figure 1—figure supplement 1.