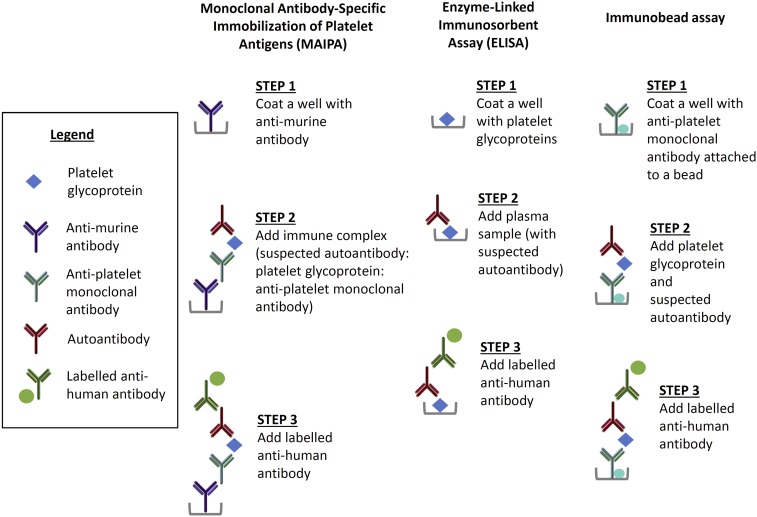
Figure 2.
The MAIPA assay can detect autoantibodies directly on the platelet surface or indirectly in the plasma. In the first step of MAIPA, a plate is coated with anti-murine antibody. In the direct assay, a patient’s platelet lysate containing the glycoprotein bound by the suspected autoantibody is mixed with an anti-platelet monoclonal antibody. For indirect MAIPA, normal platelets are mixed with patient test plasma to allow the autoantibody to bind. In the third step, the presence of an autoantibody is detected with a labeled anti-human antibody. The ELISA is an indirect assay in which a plate is coated with platelet glycoprotein followed by the patient test plasma sample. As in the MAIPA, the presence of an autoantibody is detected with a labeled anti-human antibody. The Immunobead assay can be indirect or direct, and it is a type of antigen capture assay similar to the MAIPA; the difference is that the glycoprotein is captured on the well by an anti-platelet monoclonal antibody conjugated to a bead.