Figure 1 – Ten of the genes identified as exhibiting rax-dependent expression are expressed in the developing eye.
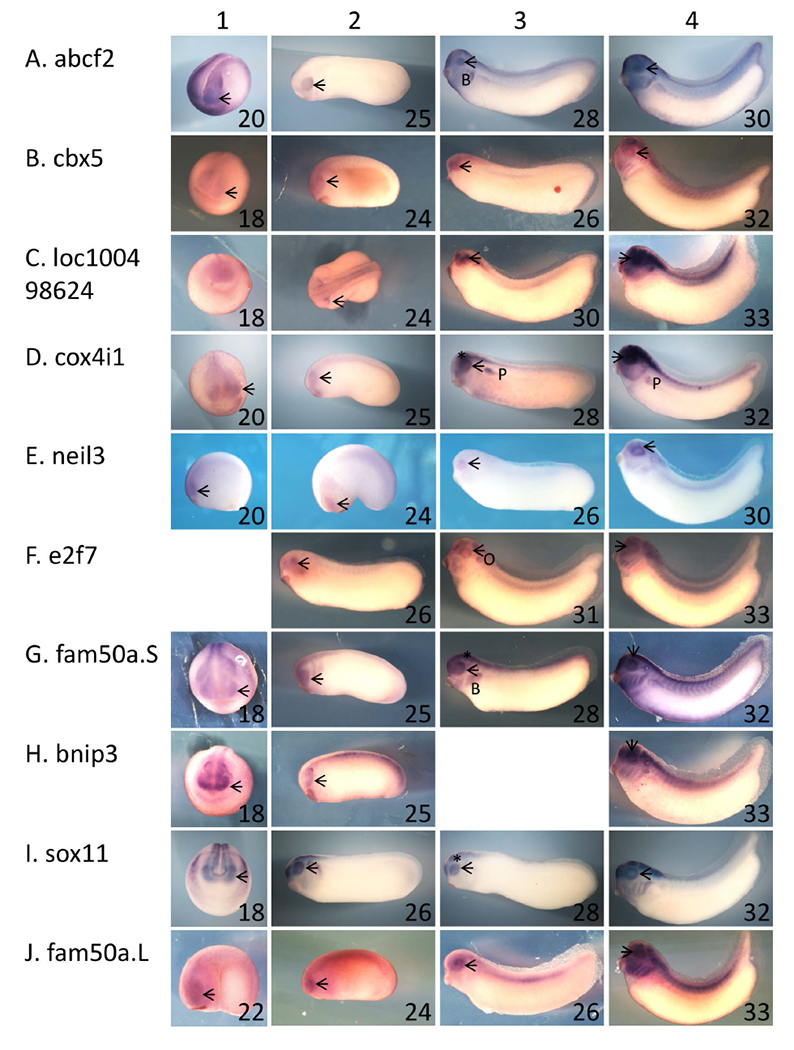
A – J: Xenopus laevis embryos were fixed and subjected to in situ hybridization using antisense riboprobes specific for 10 of the genes identified as exhibiting rax-dependent expression in the microarray screen described in the text. Genes/riboprobes are identified to the left of each row. Embryos used were late neurula (st 18 – 20, column 1), with the exception of J1 (st 22), early tailbud (st 24 and 25, column 2), mid tailbud (st 25 – 31, column 3), and mid-late tailbud (st 30 – 33, column 4). Lateral views are shown for all embryos except for A1, B1, C1, D1, G1, H1, I1, where anterior views are shown. In all cases, dorsal is towards the top of the figure. Abbreviations and marks: arrowhead – eye; * - brain; B – branchial arches; P – pronephros.
