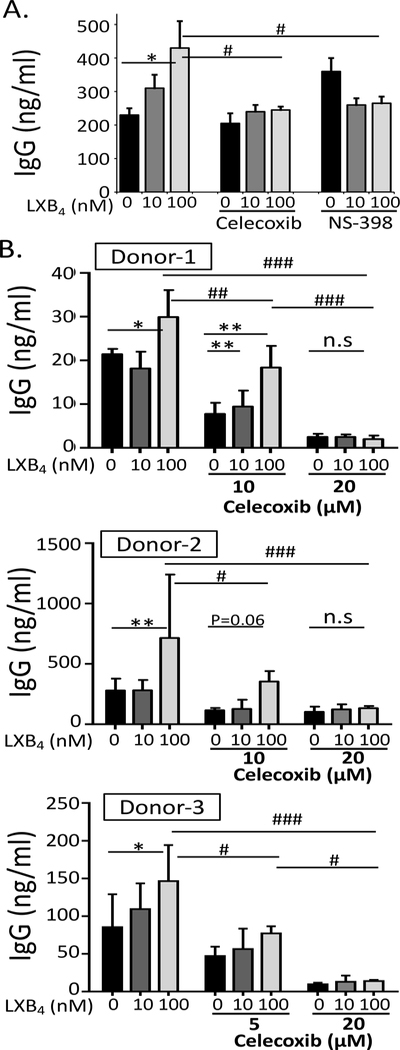
Figure 5. The stimulatory effect of LXB4 on memory B cells is mediated by COX2 activity.
(A) CD19+ B cells from healthy donors were stimulated with the memory B cell-inducing cocktail and treated with 10μM celecoxib or NS-398, prior to LXB4 treatment. Cell culture supernatants were collected at day 7–8, and IgG levels were measured by ELISA. Results shown are mean ± S.D. for triplicate wells from one representative donor of 2 donors tested. (B) B cells were stimulated with the memory B cell-inducing cocktail and treated with celecoxib at the indicated concentrations, and IgG levels were measured. Each panel is a single donor and the results shown are mean±S.D. of triplicate wells. Data analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s posttest, *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001 compared to vehicle alone. #p≤0.05, ##p≤0.01, ###p≤0.01 compared to vehicle plus 100 nM LXB4.