Fig. 11. Sex differences in the distribution of mu opioid receptor (MOR) silver-intensified gold (SIG) particles in hilar parvalbumin (PARV)-labeled interneurons in saline-injected and oxycodone condition place preference rats.
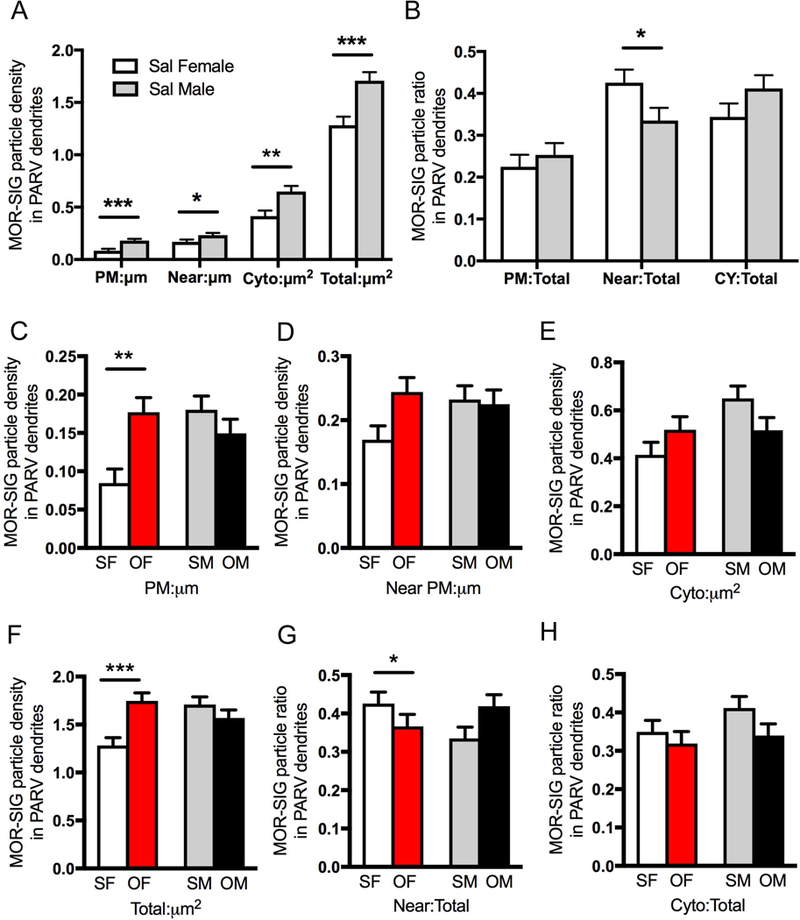
A. Sal-females compared to Sal-males have lower densities of MOR-SIG particles localized on the plasmalemma (PM), near the plasmalemma (Near), in the cytoplasm (Cyto), and in total in PARV-labeled dendrites. B. Sal-females compared to Sal-males have a significantly larger proportion of MOR-SIG particles near the plasmalemma of PARV-labeled dendrites. C-H. Density and partitioning ratios of MOR-SIG particles in the subcellular compartments of PARV-labeled dendrites are shown. Compared to Sal-females (SF), Oxy-females (OF) showed a significant increase in MOR-SIG particle density on the plasmalemma (C) and in total (F) within PARV-labeled dendrites. No differences in the partitioning ratio of MOR-SIG particles in PARV-labeled dendrites were seen in Oxy- and Sal-females. No differences in either the density or the partitioning ratio of MOR-SIG particles in PARV-labeled dendrites were seen in Sal- and Oxy-males. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05; N = 3 rats per group; n = 50 dendrites per rat.
