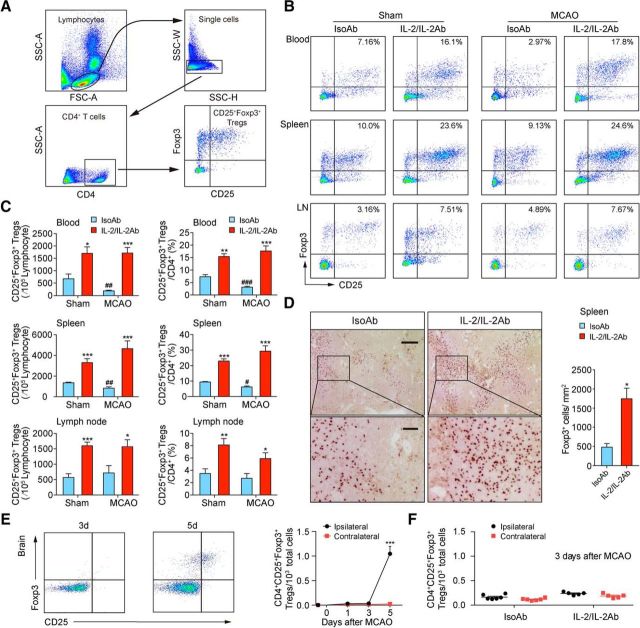
Figure 1.
IL-2/IL-2Ab treatment greatly expands the Treg population. A–C, C57BL/6 mice were treated with IL-2/IL-2Ab complex or IsoAb intraperitoneally for 3 d before 60 min MCAO or sham operation. Blood, spleen, and lymph node (LN) cells were analyzed for the expression of CD4, CD25, and Foxp3 by flow cytometry. A, Gating strategy for CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs. B, Representative flow cytometry plots of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs derived from the blood, spleen, and LN of sham (left) or MCAO (right) mice. C, Percentages of CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs among CD4+ T cells in blood, spleen, and LNs and the number of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs in 105 lymphocytes in blood, spleen, and LNs significantly increased in IL-2/IL-2Ab-treated group compared with IsoAb-treated group 3 d after MCAO or sham operation. n = 4–7/group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, IL-2/IL-2Ab versus IsoAb; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, IsoAb MCAO versus IsoAb sham. D, Immunostaining (left) and quantification (right) of Foxp3+ cells in the spleen demonstrating increased Treg number after IL-2/IL-2Ab treatment. n = 3/group. Scale bar, top, 200 μm; bottom, 50 μm. E, CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ Treg infiltration into the ischemic brain was detected by flow cytometry at the indicated time points after 60 min tMCAO. n = 3–5/group. ***p < 0.001 ipsilateral versus contralateral at the indicated time point after tMCAO. F, No significant infiltration of Tregs was detected in the ischemic brain 3 d after stroke in either IsoAb or IL-2/IL-2Ab-treated mice. n = 5–6/group.