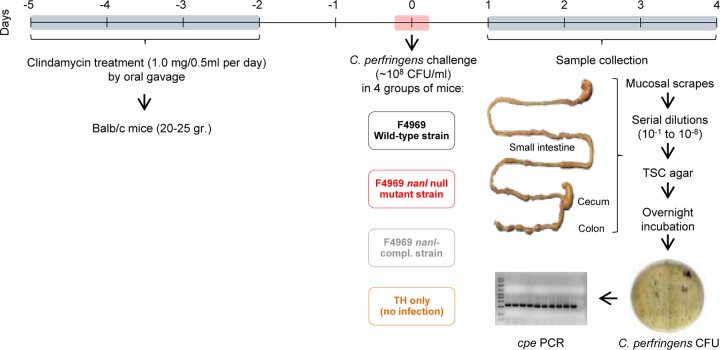
FIG 1.
Development of a mouse model for Clostridium perfringens intestinal colonization. Male or female BALB/c mice (weight, 20 to 25 g) were treated orally for 4 days with 1.0 mg of clindamycin dissolved in 0.5 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride by using sterilized oral gavage needles. After 48 h with no treatment, groups of mice were orally challenged with TH broth only (no infection) or ∼108 CFU/ml of wild-type F4969 in TH broth. Some mice were challenged with the same number of nanI null mutant or complemented cells instead of the wild type. During the following 4 days, subgroups of mice (total = 8 mice per subgroup) were euthanized daily and mucosal scrapings from the small intestine, cecum, and colon were collected and weighed. Samples were resuspended in TH medium, and serial dilutions were plated on selective TSC agar plates for C. perfringens and anaerobically incubated overnight at 37°C to calculate the number of CFU per gram of mucosal scraping. A representative number of black colonies obtained 24 h later was screened by PCR for the cpe gene. TSC, tryptose-sulfite-cycloserine medium; compl., complemented.