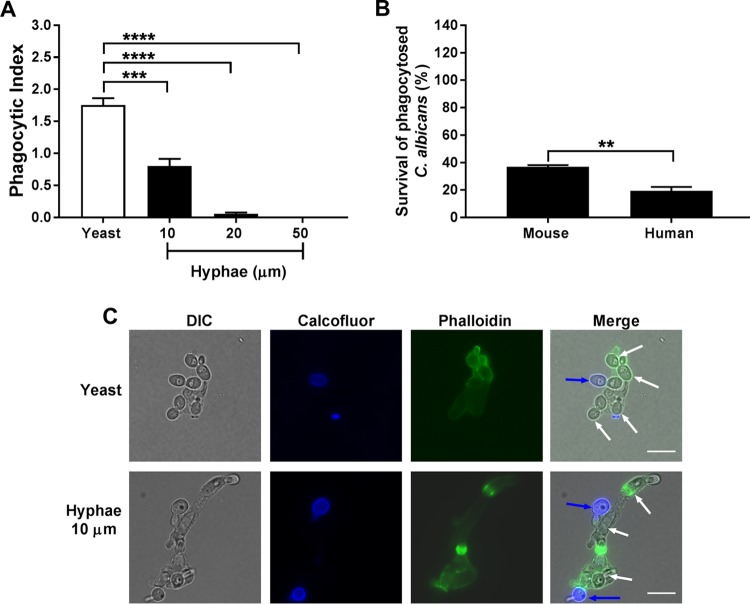
FIG 1.
Initial assessment of C. albicans phagocytosis and survival by neutrophils. (A) Human blood-derived neutrophils (H-PMNs) were infected with C. albicans yeast or 10-, 20-, or 50-μm hyphae at an MOI of 3 for 30 min. Extracellular fungal cells were stained using calcofluor, and H-PMNs were stained with phalloidin. Unstained intracellular C. albicans cells were counted in at least 100 H-PMNs, and the phagocytic index was calculated by obtaining the ratio of the total number of ingested C. albicans cells and the total number of neutrophils counted. (B) Murine or human primary neutrophils were coincubated with C. albicans at an MOI of 0.1 for 3 h. Cells were lysed and internalized C. albicans was released, plated in agar, and incubated for 48 h to obtain viable CFU. Survival was calculated as follows: (recovered C. albicans CFU after neutrophil lysis/total number of phagocytosed C. albicans cells) × 100. Results are the means ± SEs from at least three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (A) or unpaired Student's t test (B). **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. (C) Representative yeast and hyphal (average of 10 μm) phagocytosis by H-PMNs. Nonphagocytosed C. albicans cells are shown by calcofluor white staining (blue arrows), H-PMNs by phalloidin staining (green), and phagocytosed C. albicans by white arrows in merged panels. Scale bars = 10 μm.