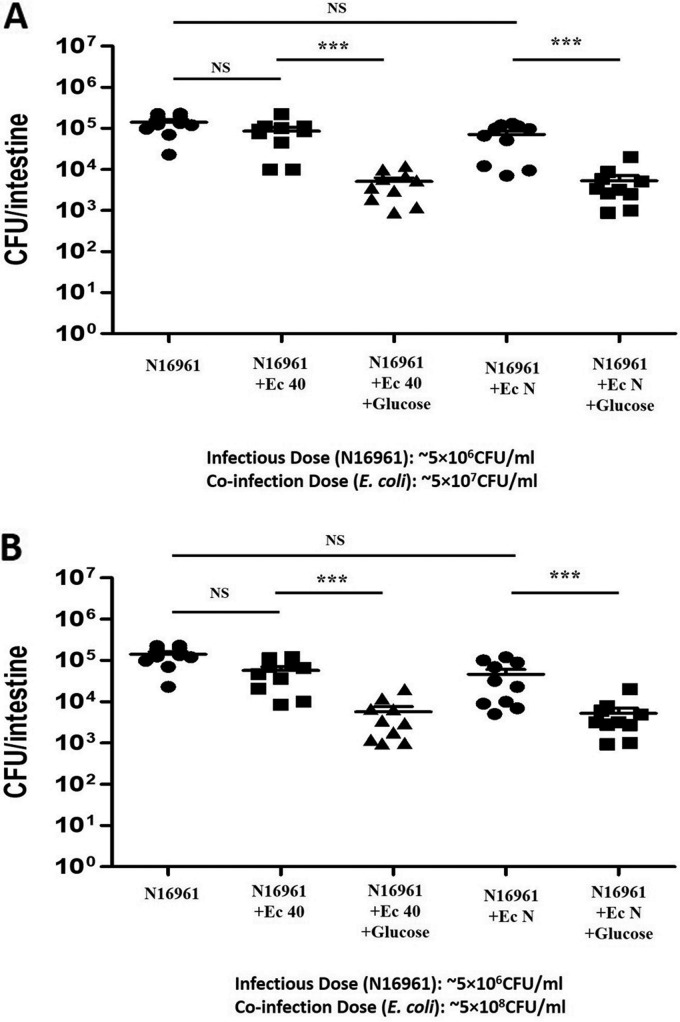
FIG 4.
Effect of different doses of E. coli strains plus glucose on V. cholerae colonization of zebrafish intestine. Zebrafish were fed 1% glucose for 12 h, and ∼5 × 107 CFU/ml or ∼5 × 108 CFU/ml of E. coli 40 or N was coinoculated with ∼5 × 106 CFU/ml of either V. cholerae O395 or N16961. The ratio of the coinfection of E. coli to V. cholerae was 10:1 (A) or 100:1 (B). The same N16961 control group was used during both experiments, and these results are shown in both panels to facilitate comparisons. V. cholerae levels were determined by plating of serial dilutions of the intestinal homogenates. ***, P < 0.0001; NS, nonsignificant differences.