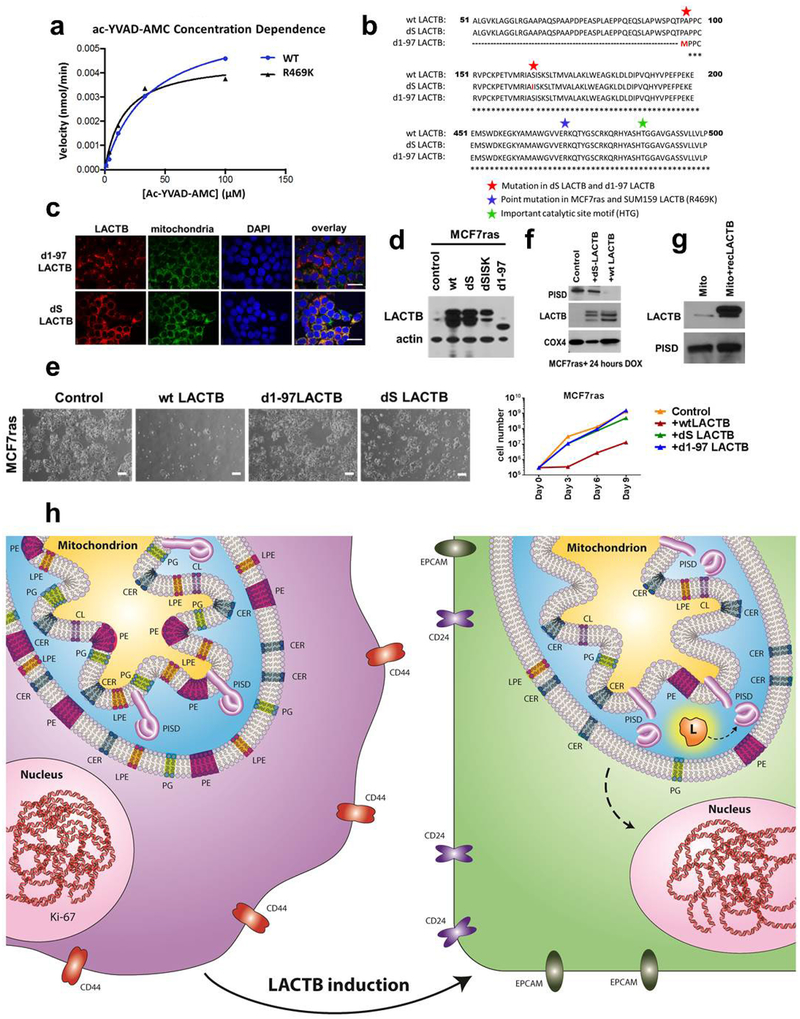
Extended Data Figure 10 |. LACTB mutagenesis.
a, Related to Fig. 5c. Velocity of the ac-YVAD-AMC enzymatic reaction in relation to substrate concentration for wild-type LACTB and mutant LACTB(R469K). b, Comparison of amino acid sequence of wild-type (WT) LACTB, LACTB(S164I) (catalytic site LACTB mutant, where an essential serine residue was replaced by an isoleucine, labelled in image as dS LACTB) and LACTB(Δ1−97) (mitochondrial localization mutant, labelled in the image as d1–97LACTB. as described in ref. 8). Only a partial sequence of LACTB is shown. The points of the mutation of LACTB(S164I) and LACTB(Δ1–97) are highlighted in red and marked by a red star symbol. The blue star symbol marks the site of the R469K mutation in endogenous LACTB from MCF7-RAS and SUM159 cells. The green star symbol marks the site of a notable substrate docking site in LACTB. c, Immunofluorescence analysis of MCF7-RAS–Tet/ON-LACTB(S164I) and MCF7-RAS–Tet/ON-LACTB(Δ1−97) cells, where DOX was added for 24 h. Cells were stained with mitochondrial marker (green), a LACTB marker (red) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 30 μm. d, Western blot analysis of expression levels of LACTB in control MCF7-RAS cells and MCF7-RAS–Tet/ON-LACTB (wild-type LACTB, LACTB(S164I), LACTB(Δ1−97), LACTB(ΔSISK)) cells where DOX was added for 24 h. The LACTB(ΔSISK) mutant contains a deletion of 4 amino acid residues in catalytic site of LACTB. The expression level of this mutant was unstable, therefore we did not include this mutant in our study. e, Proliferation rates of control MCF7-RAS cells and MCF7-RAS–Tet/ON-LACTB (wild-type LACTB, LACTB(S164I), LACTB(Δ1−97)) cells upon addition of DOX for the indicated number of days. Pictures were taken at six days of DOX induction. Scale bars, 200 μm. f, Western blot analysis of PISD expression in mitochondria isolated from MCF7-RAS and MCF7-RAS–Tet/ON-LACTB (wild-type LACTB and LACTB(S164I)) cells where DOX was added for 24 h to all groups. g, Western blot analysis of PISD levels after in vitro incubation of permeabilized mitochondria (isolated from MCF7-RAS cells) with or without addition of recombinant LACTB (isolated from HEK293T cells). h, Graphical abstract. LACTB induction leads to a change in cancer cell state. As such, a proliferative, less differentiated cancer cell turns into a non-tumorigenic differentiated cancer cell upon LACTB induction. This is characterized by an initial disappearance of the proliferation marker Ki-67, followed by downregulation of the stem-cell marker CD44 and increased expression of the differentiated epithelial markers CD24 and EPCAM. This is achieved through the ability of LACTB to decrease the protein expression levels of the mitochondrial enzyme PISD and subsequent changes in mitochondrial PE and/or LPE levels.