Figure 4.
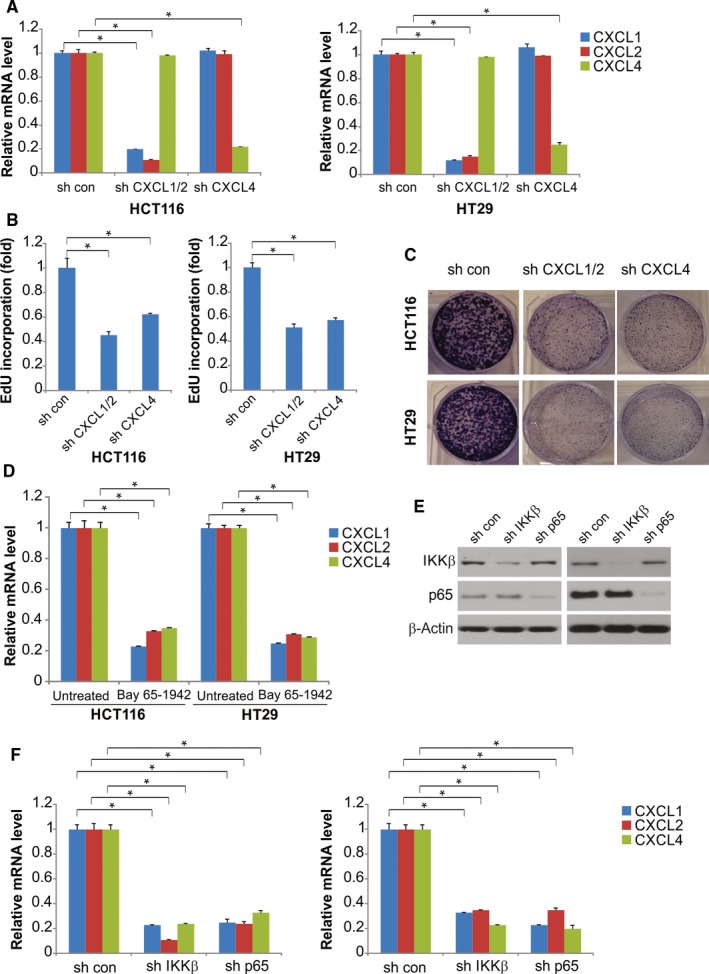
GNA13 induces CXCL2, CXCL1, and CXCL4 expression through the IKKβ‐NF‐κB pathway. A, HCT116 and HT29 cervical cancer cells were transfected with CXCL1/2, CXCL4, or control shRNA; after 48 h of transfection, expression of CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL4 was quantified by qRT‐PCR. B, In the EdU incorporation assay, 2 d after transfection, reduced expression of CXCL1, CXCL2, or CXCL4 due to shRNAs inhibited HT29 and HCT116 cell proliferation compared with that in the cells transfected with control shRNA. C, Suppression of CXCL1, CXCL2, or CXCL4 by shRNAs inhibits the clonogenic growth of HCT116 and HT29 cells. D, Expression of CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL4 mRNA in HCT116 and HT29 cells treated with 2 μm IKKβ inhibitor Bay 65‐1942 or the control was analyzed by qRT‐PCR. E, IKKβ and NF‐κB p65 protein expression was quantified by Western blotting. F, HT29 and HCT116 cells were transfected with shRNA against IKKβ, NF‐κB p65, or the control, after 48 h of transfection, and then expression of CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL4 mRNA was quantified by qRT‐PCR. *, P < 0.05
