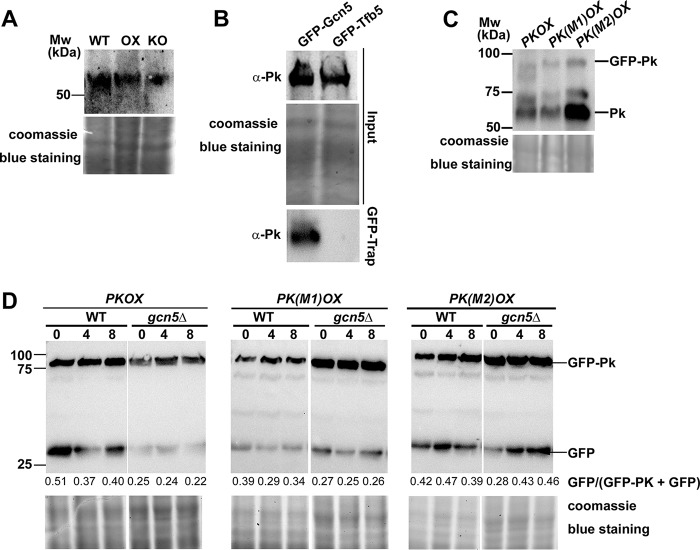
FIG 4.
Gcn5 interacts with Pk and may be responsible for Pk stability. (A) Total protein lysates were extracted from wild-type (WT), GCN5OX (OX), and gcn5Δ (KO) strains, and then analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-PK antibodies (rabbit; 1:500; Abcam, ab34554). Detection of a single band higher than the 50-kDa molecular marker band corresponds to Pk protein. Coomassie blue staining of SDS-PAGE of total proteins served as a loading control. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation assays among Gcn5 and Pk proteins. The M. oryzae strains carrying GFP-Gcn5 or GFP-Tfb5 were grown in liquid CM at 28°C for 48 h. Total proteins extracted from the strains were subjected to immunoprecipitation with GFP-Trap (Chromo Tek, gta-20), and the IP proteins were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE and detected by anti-Pk antibody (α-Pk). Coomassie blue staining of SDS-PAGE of total proteins served as a loading control for input proteins. (C) Total protein lysates were extracted from the M. oryzae strains carrying PKOX, PK(M1)OX, and PK(M2)OX and then analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-PK antibodies. The fused GFP-Pk protein and the Pk peptide alone were detected, judged by the molecular weight (Mw) as shown. Coomassie blue staining of SDS-PAGE of total proteins served as a loading control. (D) Total protein lysates were extracted from the M. oryzae strains carrying PKOX, PK(M1)OX, and PK(M2)OX, in both WT or gcn5Δ background, in a time course of 0, 4, and 8 h after treatment with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog no. C104450). Detection of the fused GFP-Pk protein and GFP peptide alone was labeled. The extent of Pk degradation was estimated by calculating the amount of free GFP compared with the total amount of intact GFP-Pk and free GFP (the numbers appear below the blot). Densitometric analysis was performed using ImageJ (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/). Coomassie blue staining of SDS-PAGE of total proteins served as a loading control.