Figure 3.
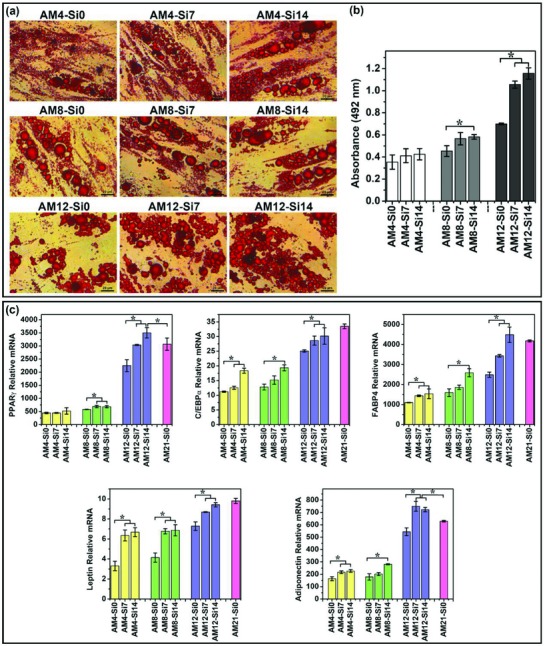
The effects of Si ion as a differentiation enhancer on the stimulation of adipogenic differentiation. a) Oil Red O staining of cells showed that Si ions stimulated the increase of lipid accumulation. Lipid droplets were stained in red. Scale bar, 20 µm. b) Quantitative analysis of Oil Red O staining showed that Si ions significantly stimulated lipid accumulation (n = 3 for both the groups; *p < 0.05). c) Quantitative PCR analysis showed that Si ions enhanced the adipogenic marker gene of PPARγ, C/EBPα, FABP4, leptin, and adiponectin expression of HBMSCs (n = 3 for both the groups; *p < 0.05). AM4‐Si7, AM4‐Si14: HBMSCs cultured with adipogenic differentiation medium alone for 4 days, and then further cultured up to 21 days in growth medium containing different concentrations of Si ions (0, 7, and 14 µg mL−1), respectively; AM8‐Si0, AM8‐Si7, AM8‐Si14: HBMSCs cultured with adipogenic differentiation medium alone for 8 days, and then further cultured up to 21 days in growth medium containing different concentrations of Si ions (0, 7, and 14 µg mL−1), respectively; AM12‐Si0, AM12‐Si7, AM12‐Si14: HBMSCs cultured with adipogenic differentiation medium alone for 12 days, and then further cultured up to 21 days in growth medium containing different concentrations of Si ions (0, 7, and 14 µg mL−1), respectively; AM21‐Si0: HBMSCs cultured in adipogenic differentiation medium without Si ions for 21 days.
