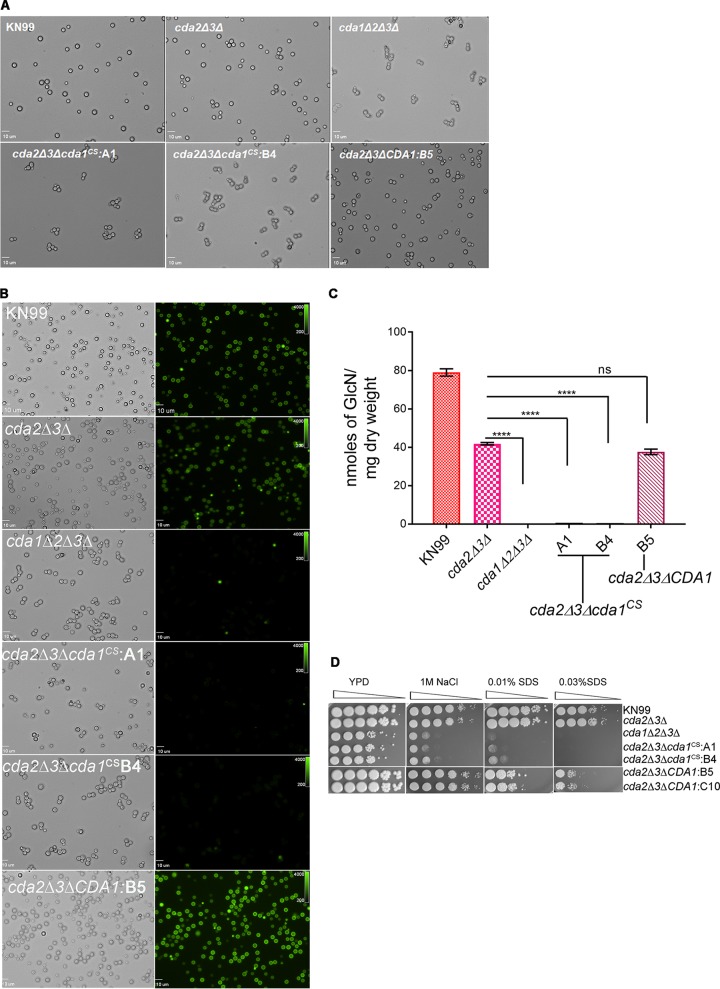
FIG 6.
Point mutations in the catalytic site of Cda1 expressed in a cda2Δ3Δ strain results in chitosan deficiency and phenotypes similar to those of the chitosan-deficient cda1Δ2Δ3Δ strain. (A) Cda1 catalytic point mutant strains generated in the cda2Δ3Δ background display a budding defect when grown in YPD medium similar to the budding defect observed for a chitosan-deficient cda1Δ2Δ3Δ strain. The wild-type and mutant strains were grown in YPD for 36 h, collected, washed, and visualized with an Olympus BX61 microscope, and photographs were taken at 100× magnification. (B) The wild-type, corresponding Cda deletion, and mutant strains were grown as described above in panel A and stained with Eosin Y to detect cell wall chitosan. Bright-field and fluorescence isothiocyanate panels are shown. Photographs were taken at 100× magnification. (C) Quantitative determination of cell wall chitosan in wild-type and various Cda deletion and mutant strains by the MBTH assay. Cells were grown in YPD for 48 h, collected, washed, and used for the assay. Data represent the averages for three biological and two technical replicates. Significant differences between the groups were compared by one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (****, P < 0.0001 comparing the chitosan amount for each strain to that for the cda2Δ3Δ strain). (D) Wild-type and various C. neoformans Cda deletion and catalytic point mutant strains were grown in YPD for 36 h. Cells were harvested, washed, and diluted to an OD650 of 1.0. Four microliters of 10-fold serially diluted cell suspension was spotted on YPD agar alone and YPD agar containing cell wall stress reagents NaCl and SDS. The plates were incubated for 4 days at 30°C and photographed.