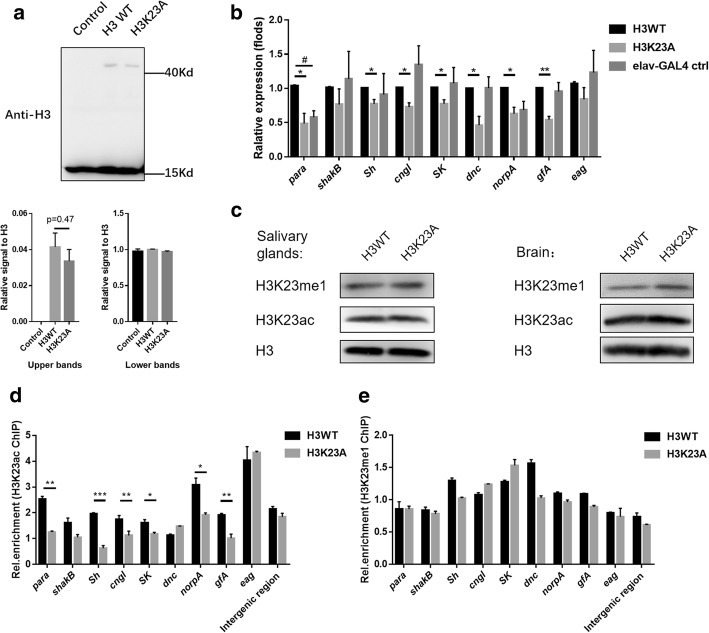
Fig. 2.
Decreased H3K23ac levels impair neuronal gene activation in H3K23A mutants. a A western blotting was used to calculate the ratio of exogenous H3. The data was measured by the software Image J. N=3 biological replicates. b The expression levels of neuronal genes were examined by RT-qPCR in the larval brains. The mRNA levels of neuronal genes were normalized to the levels of rp49. Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction was used. N=3 biological replicates. c The H3K23ac and the H3K23me1 levels are examined by western blotting. The samples were collected from salivary gland and larval brains, respectively. d-e The H3K23A mutation reduces the occupancy of the H3K23ac marker in the neuronal genes. The enrichment of H3K23ac and H3K23me1 were normalized to input. The intergenic region was used as the euchromatic control region. Unpaired t-test was used. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (N=2 biological replicates). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, #p<0.05 (elav-GAL4 group compared to H3WT group)