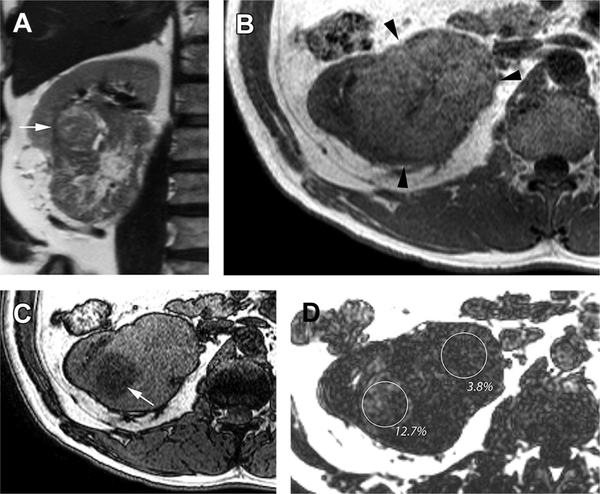
Fig. 1.
Heterogeneous lipid accumulation in high-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma (Fuhrman grade 3). (A) Coronal T2-weighted SSTSE image shows a large hetero-geneous right renal mass with a more focal nodule in the superolateral aspect of the mass (arrow). (B) Axial T1-weighted in-phase gradient-echo image through the level of the nodule (A) shows near-uniform moderately hyperintense signal intensity relative to renal cortex in the mass (arrowheads). (C) Axial T1-weighted gradient-echo opposed-phase image, at the same anatomic level as in (B), shows marked diffuse drop in signal intensity in the region well defined nodule (arrow), indicating the presence of intravoxel fat. (D) Fat fraction map calculated from a 3-D T1-weighted, multiecho, multipoint Dixon technique confirms and quantifies the presence of intravoxel fat within the mass. Note the high fat fraction (12.7%) in the nodule compared with the lower fat level in rest of the mass (3.8%). The tumor showed histopathologic features consistent with the presence of greater fat content within the nodule.