Figure 2: Vitamin E conjugation enhances lymphatic drainage and immunogenicity of molecular vaccines.
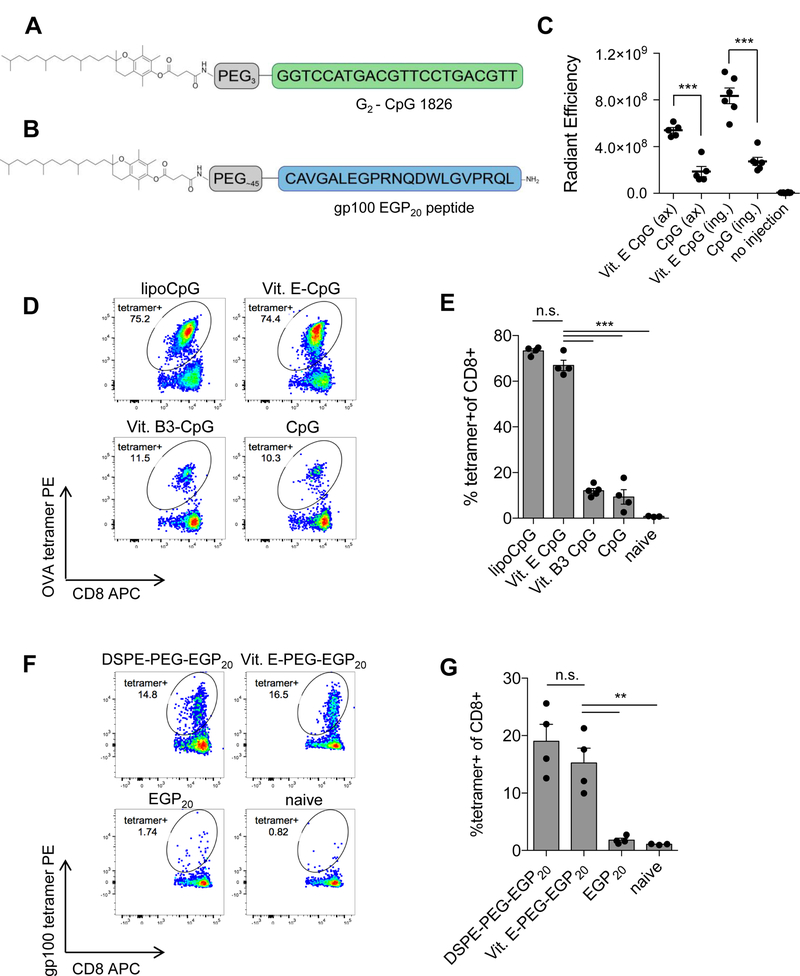
A, Schematic of vitamin E linked to CpG 1826 via triethylene glycol spacer. B, Schematic of EGP20 peptide linked to vitamin E via PEG spacer. C, Mice were injected subcutaneously with 3.3 nmol TAMRA-labeled CpG or lipo-CpG. Axillary (ax) and inguinal (ing) nodes were resected 24 hours later. Uptake was quantified using IVIS. Shown is background-subtracted radiant efficiency. n = 5–6/group; student’s t-test. D-E, Mice were primed on day 0 and boosted on day 14 with 10µg OVA and 1.24 nmol of CpG or CpG conjugate. Tetramer staining was performed on day 21. D, Representative plots gated on live CD8+ T cells. E, Mean tetramer responses quantified as % tetramer+ of CD8+. n = 4/group; ANOVA with Tukey post-test; representative of 2 independent experiments. F-G, C57BL6/J mice were primed on day 0 and boosted on day 14 with 5 nmol EGP20 peptide or EGP20-conjugate and 25 µg c-di-GMP. Tetramer staining was performed 7 days post-boost. F, Representative plots gated on live CD8+ T cells. G, Mean tetramer responses quantified as % tetramer+ of CD8+ n = 4/group; ANOVA with Tukey post-test; representative of 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
