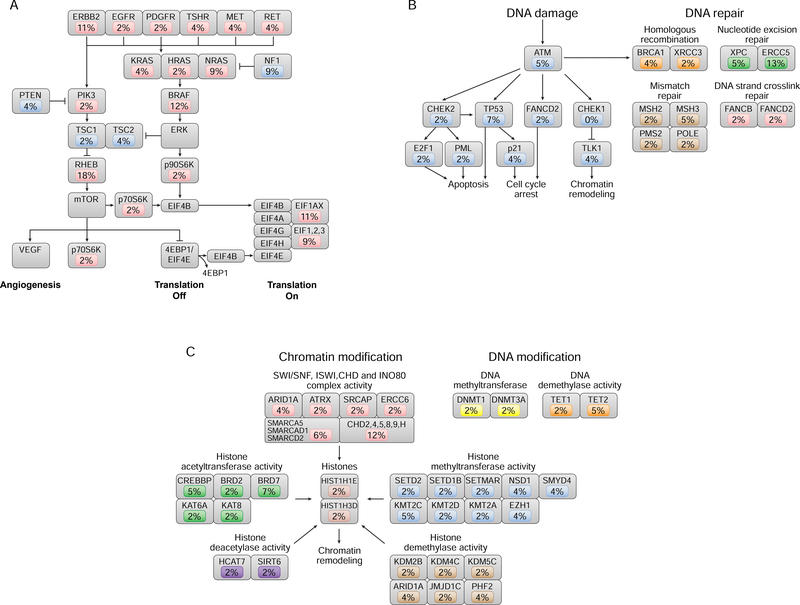
Figure 2. Somatic mutations of the canonical signal transduction and tumor suppressor pathways in HCC.
(A) RAS/RAF/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway mutations occurred in 55% of tumors, and the incidence of mutation in each component of the pathway is indicated. Oncogenic alterations are shown in red; tumor suppressor alterations are shown in blue. All alterations were somatic mutations, with the exception of amplification events for RHEB and BRAF and deletion events for NF1. (B) DNA damage and DNA repair pathways were mutated in 38% of tumors, and the incidence of mutation in each component of the pathway is indicated. Gene mutations involved in DNA damage are shown in blue. Mutations in DNA repair pathways occurred in homologous recombination (orange), nucleotide excision repair (green), mismatch repair (brown), and DNA strand cross-link repair (red). (C) Epigenetic-modifying gene mutations occurred in 33 tumors (59%), by either chromatin modification (55%) or DNA modification (9%); the incidence of mutation in each component of the pathway is indicated. Chromatin-modifying mutations occurred in chromatin-modifying complexes, such as the SWI/SNF complex (red), histone acetyltransferases (green), methyltransferases (blue), histone deacetylases (purple), and demethylases (brown), as well as in histones themselves. DNAmodifying mutations occurred in DNA methyltransferases (yellow) and demethylases (orange).