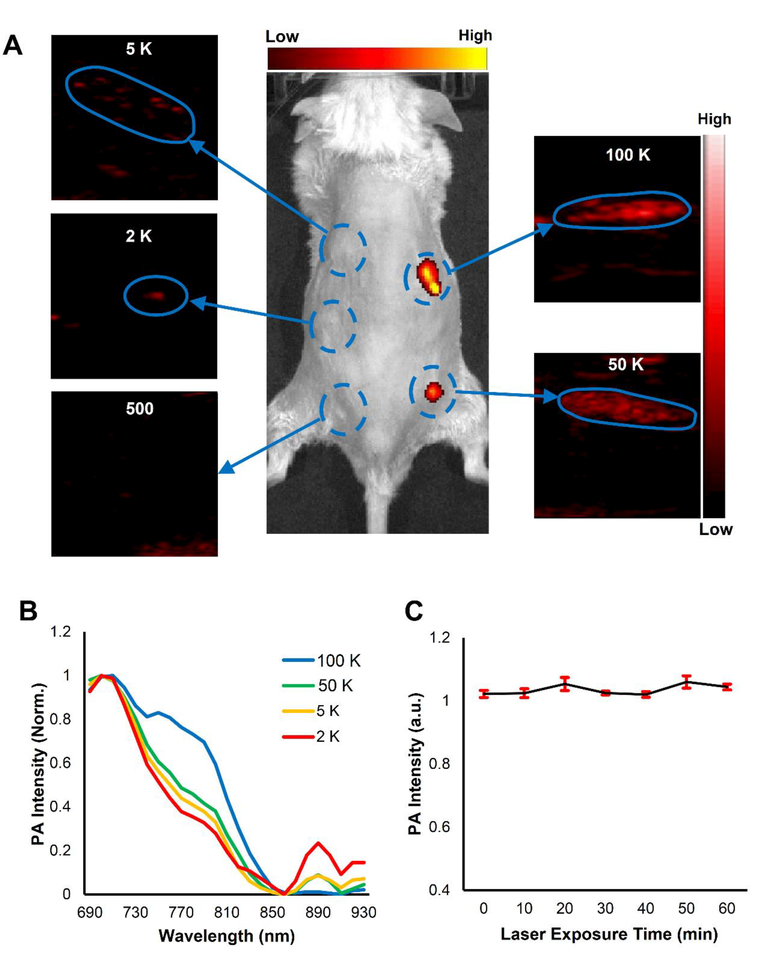
Figure 4. PANPs enabled PAI to detect a small number of labeled cells in vivo.
Five groups with different numbers of PANP-labeled hESC-CMs (500/2,000/5,000/50,000 /100,000) were mixed with 10 μL Matrigel, respectively, and subcutaneously injected into mice. (A) While fluorescent imaging only detected the cell numbers of 50,000 or more, PAI was able to detect the cell numbers as few as 2,000 by virtue of the strong PA signals and specific PA spectrum of PANPs. (B) Different numbers of PANP-labeled cells showed a similar PA spectral pattern in vivo, which was a notable feature to distinguish these cells from background tissues. (C) The excited PA signals from PANPs were quite stable even under a continuous PAI for up to 1 hour.