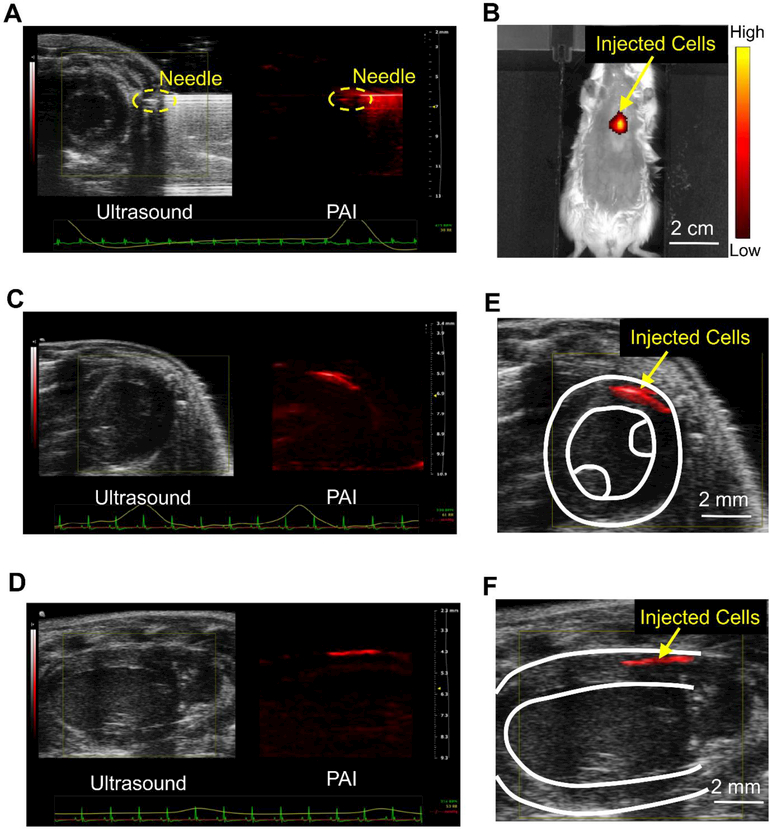
Figure 5. PAI of the injection and engraftment of the PANP-labeled hESC-CMs in mouse hearts in vivo.
(A) Labeled hESC-CMs were intramyocardially injected into a mouse heart with an engineered hydrogel under a real-time guidance with PAI and B-mode ultrasound. The ultrasound image provides cardiac structures in a short-axis view and the PA image provides needle position simultaneously. (B) The transplanted cells were imaged by fluorescence imaging (FI) in vivo using the emitted near-infrared fluorescence (peak 820 nm) from PANPs. (C-D) Using an electrocardiogram (ECG) and respiratory coupling, B-mode ultrasound and multi-spectral PA imaging were performed to image the engraftment of the PANP-labeled hESC-CMs from short-axis and long-axis views, respectively. (E-F) Merged ultrasound and PA images showed the 3D spatial relationship between the transplanted cells and the host myocardium at a high resolution (~100 μm).