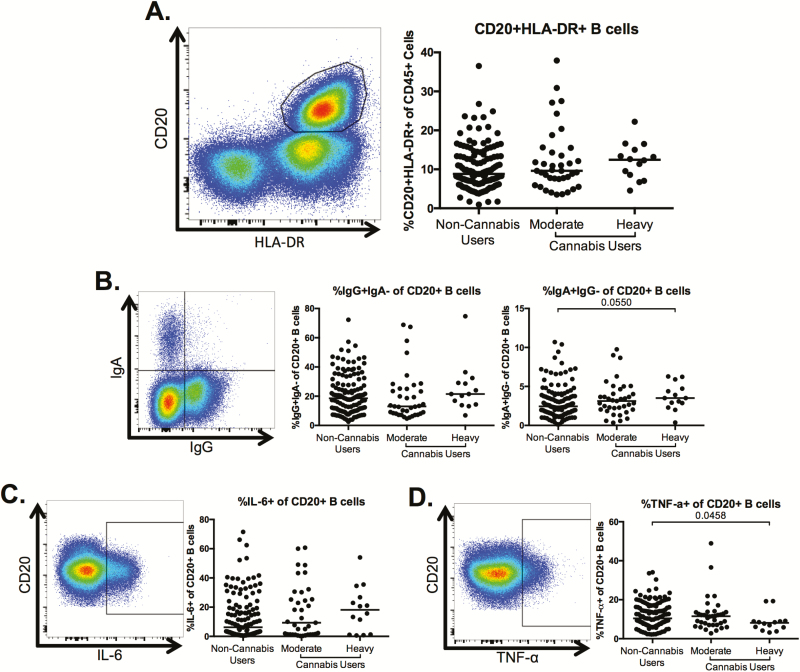
Figure 3.
B-cell frequency, isotype, and cytokine production in heavy users of cannabis compared to nonusers. Multiparameter flow cytometry was used to identify the frequency of CD20+human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR+ B cells within total peripheral blood mononuclear cells of cannabis-using and non-cannabis-using individuals. A, Representative staining demonstrating the CD20+HLA-DR+ B-cell population. Cells were identified by first excluding doublets using forward and side scatter properties, gating on total leukocytes as determined by CD45 expression and removing dead cells with an Aqua Live/Dead viability dye. The frequency of B cells was then determined by gating on CD3– cells and identifying CD20+HLA-DR+ cells within this subset. Pooled data shows the percentage of CD20+HLA-DR+ B cells in all individuals. B–D, Frequency of immunoglobulin G (IgG)+, immunoglobulin A (IgA)– and IgA+IgG– (B) cells and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)– (C) and interleukin 6 (IL-6)–producing cells (D) within the B-cell population. Pooled data is accompanied by a representative flow plot showing gating for the indicated markers. In all plots, individuals are classified as noncannabis users or cannabis users stratified by moderate or heavy cannabis use as determined by plasma quantities of 11-nor-carboxy-tetrahydrocannabinol. Each individual is represented by a single point. Horizontal bars indicate the median value. The statistical significance of differences between each of the cannabis-using groups and the noncannabis users was determined using the Mann-Whitney test.