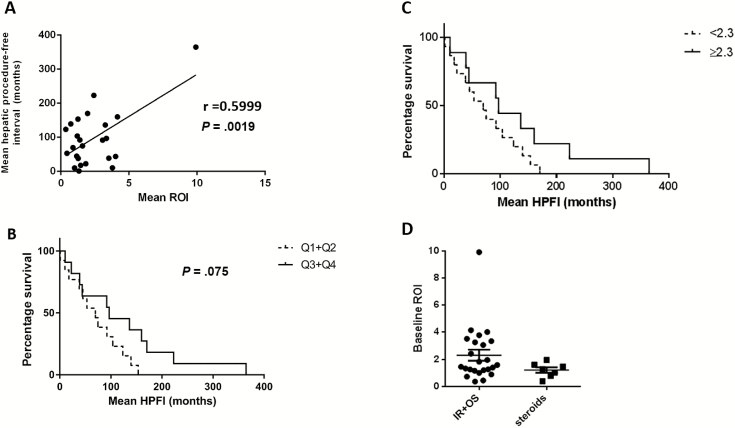
Figure 5.
A, Baseline residual reactive oxygen intermediate (ROI) levels (superoxide nmol/hour) are correlated with time to repeat hepatic intervention in patients with chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) with liver abscesses (Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, r = 0.5999, 2-tailed P value). Surgical outcome measured by time to repeat hepatic intervention in CGD patients with liver abscesses by previously defined ROI quartiles (in superoxide nmol/hour) predictive of poor outcome (Q1 and Q2 [0.26–0.94 and 0.95–1.67, respectively] vs Q3 and Q4 [1.70–2.71 and 2.72–60.5, respectively]) (B), or by low vs high preoperative residual neutrophil function (ROI <2.3 nmol superoxide/hour [dashed line] vs ≥2.3 nmol superoxide/hour ROI levels) (C). Hepatic procedure-free interval (HPFI) mean of any hepatic intervention for each patient. Patients who received corticosteroids had similar baseline neutrophil function compared to patients who underwent interventional radiology (IR) or open surgery (OS) (D) (mean baseline ROI in neutrophils and monocytes, 2.12 nmol superoxide/106 cells vs steroids, 1.64 nmol superoxide/106; Mann-Whitney U test, 2-tailed P = .202).