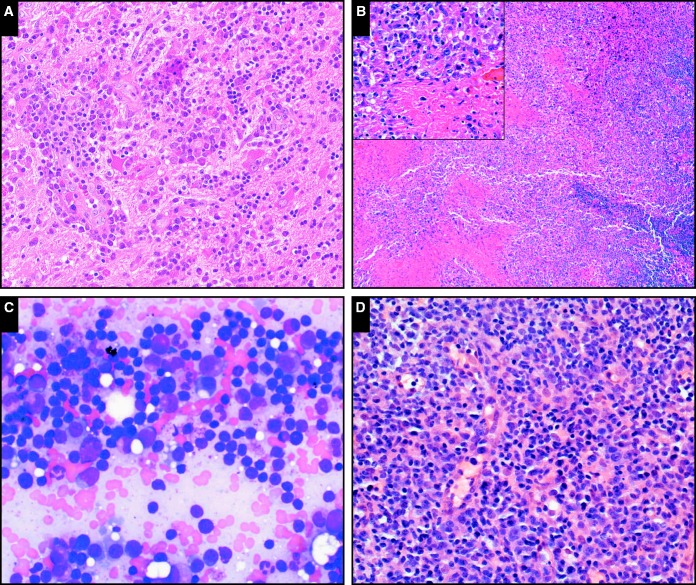
Image 1.
The full range of immunodeficiency-related B-cell lymphoproliferations described in the posttransplant setting are also seen in the setting of primary immunodeficiency. A, Plasmacytic hyperplasia involving the brain in a patient with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID; case SH2015-467) (H&E, x20). B, Epstein-Barr virus–positive mucocutaneous ulcer in a patient with CHARGE (coloboma of the eye, heart defects, atresia of the choanae, retardation of growth and/or development, genital and/or urinary anomalies, and ear malformations) syndrome (case SH2015-178); note the sheets of atypical cells surrounding areas of necrosis (inset, including forms with Hodgkin-like morphology; x20); the cuff of small mature lymphocytes is visible at right (H&E, x4). C, Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma involving the bone marrow of a patient with CVID (SH2015-223) resembles that seen in nonimmunodeficiency settings; here the lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate is visualized in a bone marrow aspirate smear (Giemsa, x40). D, Polymorphic B lymphoproliferative disorder in a patient with CVID (SH2015-82); shows scattered large atypical cells in a background of small lymphocytes and plasma cells (H&E, x20).