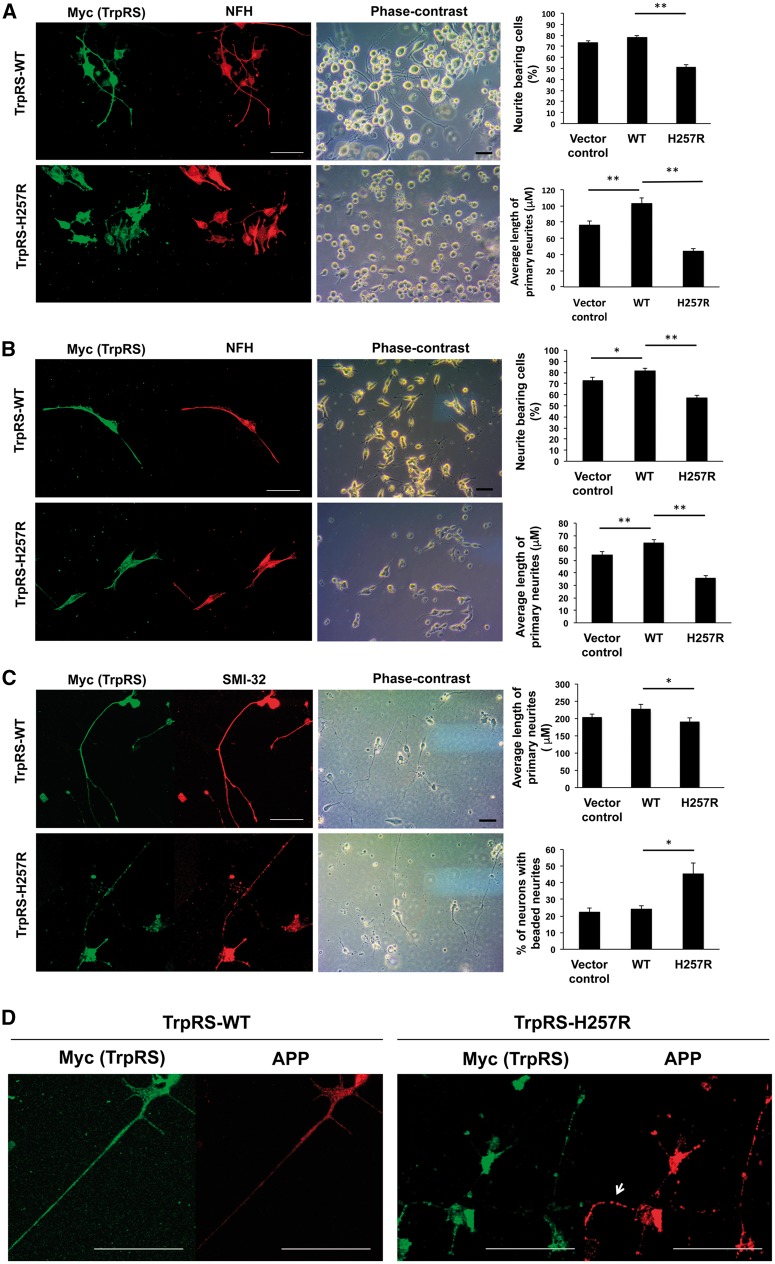
Figure 4.
His257Arg (H257R) TrpRS inhibits neurite outgrowth and leads to neurite degeneration. Neuro-2a (N2a) (A) or SH-SY5Y (B) cells were transfected with expression vector containing wild-type (WT) or H257R TrpRS or empty vector (vector control), grown under differentiation conditions, and immunostained against Myc (exogenous TrpRS staining) and neurofilament heavy polypeptide (NFH; neurite staining) at 72 h post-transfection. The representative fluorescence-immunostaining and phase-contrast images were shown, along with statistical results of per cent of cells bearing neurites and average primary neurite length. Scale bar = 50 μm. At least 100 cells from three independent experiments were measured for each preparation and data were expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *P-value < 0.05; **P-value < 0.01 when compared to wild-type. (C) Rat motor neurons (embryonic Day 14) were transfected with expression vector containing wild-type or H257R TrpRS or empty vector, and processed for immunostaining using antibodies against Myc and SMI-32 (staining for motor neurons and their neurites) at 72 h post transfection. The representative fluorescence-immunostaining and phase-contrast images were shown. Neurites of motor neurons were traced and measured, and the average primary neurite length and per cent of cells bearing beaded neurites were estimated. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments with at least 50 cells. (D) Rat motor neurons expressing above TrpRS constructs were processed for immunofluorescence analysis using antibody against amyloid precursor protein (APP; neurodegeneration staining) at 72 h post-transfection. Motor neurons expressing wild-type TrpRS showed only a faint or punctate staining of APP in the neurites, while motor neurons expressing TrpRS appeared to accumulate APP at neurites (arrow).