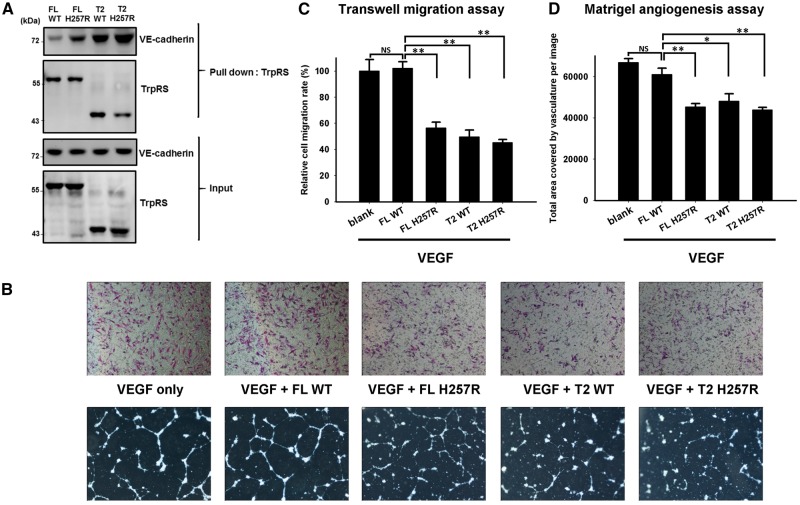
Figure 5.
Pull-down assay and in vitro angiogenesis assays showing that human His257Arg (H257R) mutant TrpRS has an augmented angiostatic effect through binding to VE-cadherin. (A) An in vitro pull-down assay used to assess the ability of His-tagged TrpRS to bind to Flag-tagged VE-cadherin. The immunoblots showed that both the full-length (FL) and the T2-H257R TrpRSs had a substantial increase in affinity to VE-cadherin compared to wild-type (WT) TrpRS. (B) Effect of the p.His257Arg mutation on the angiostatic activity of TrpRS evaluated by transwell migration assay and Matrigel angiogenesis assay using HUVECs under 16 h of VEGF165 stimulation with or without TrpRS treatment. Top: Representative microscopic images of the underside of the transwell assay membranes; Bottom: representative microscopic images of tube formation on Matrigel®. (C) Quantification of migration of HUVECs after 16 h treatment with VEGF165 and the indicated conditions of three independent experiments. Treatment with full-length H257R TrpRS, T2-H257R TrpRS, or T2-wild-type TrpRS significantly reduced in vitro cell mobility, while full-length wild-type TrpRS application did not further inhibit the cell migration compared to a control treatment of VEGF165 alone. The error bars represent standard errors of the mean (n = 3) and asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, NS = non-significant). (D) Quantification of vessel coverage (the total microscopic area covered by HUVEC vasculature) after 16 h treatment with VEGF165 and the indicated conditions of three independent experiments. The data revealed that full-length H257R TrpRS, T2-wild-type or T2-H257R TrpRS could significantly inhibit angiogenesis. Treatment of full-length wild-type TrpRS did not show inhibitory effect on tube formation.