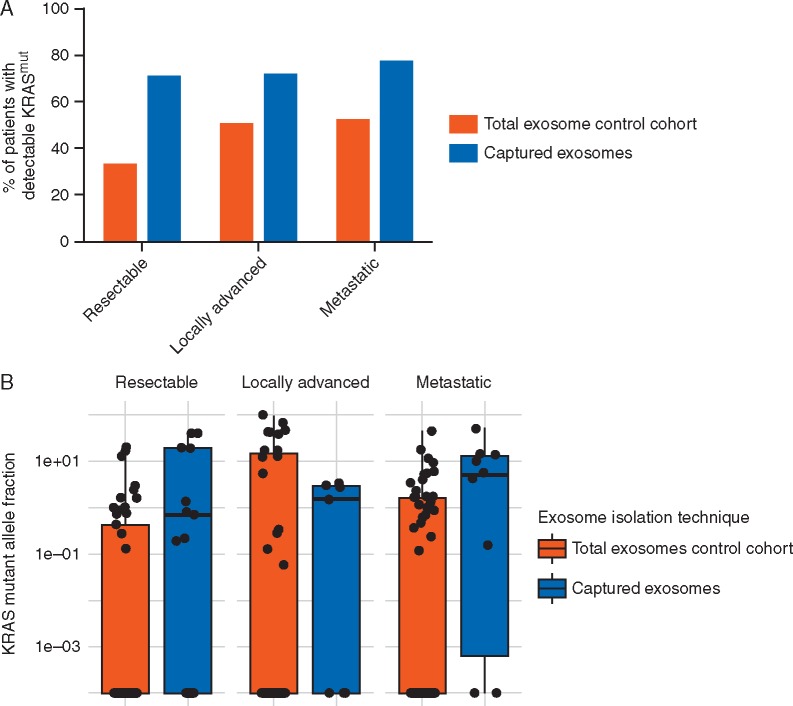
Figure 2.
exoDNA KRAS mutant detection in circulation. (A) Percent of patients with detectable mutant KRAS in exoDNA among those patient samples that did and did not undergo capture enrichment. When comparing the percentages of patients with detectable KRAS in the pulldown-cohort versus the total exosome cohort, the pulldown-cohort consistently detects KRAS in a higher proportion of patients across stages. This increase in call-rate was statistically significant in resectable patients (P = 0.024) where pulldown samples were 4.11 (95% CI: 1.14–17.19) more likely to have KRAS detected. (B) KRAS mutant allele frequency (MAF) comparisons of captured exosomes versus total exosomes, there was a statistically significant difference showing increased KRAS MAFs from the captured exosomes for resectable and metastatic patients (P = 0.003 and 0.015, respectively, using one-sided Wilcoxon Rank Sum tests).