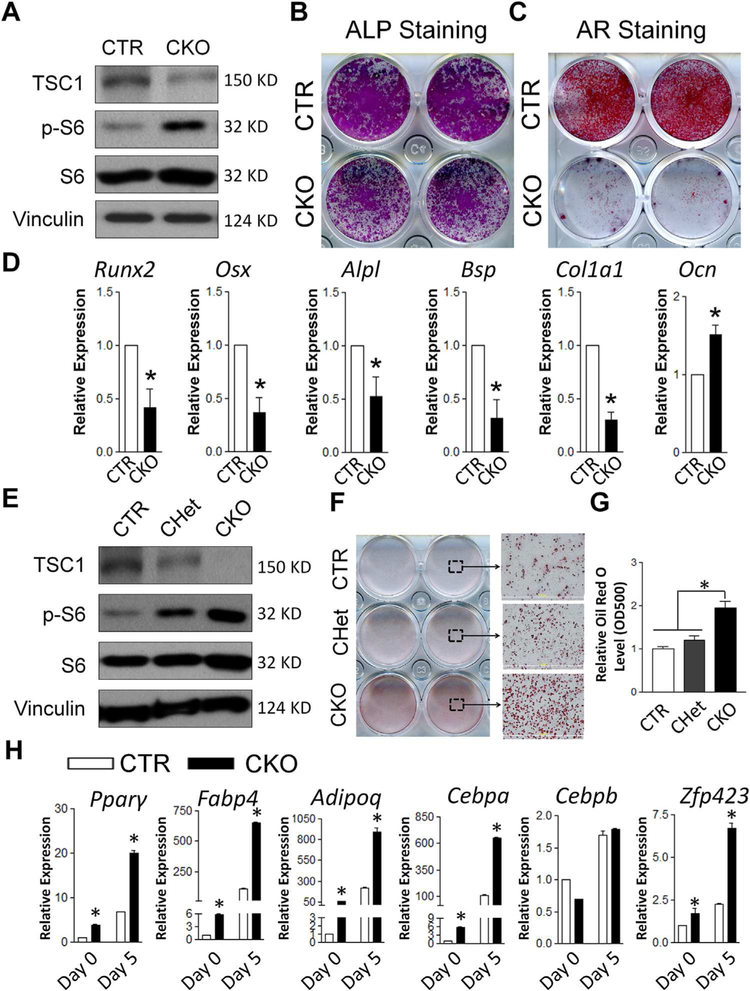
Fig. 5.
Tsc1 deletion leads to compromised osteogenic and enhanced adipogenic differentiation in BMSCs. (A) TSC1 was effectively deleted in CKO BMSCs as shown by Western blot. (B, C) Osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs were analyzed by ALP staining at day 7 (B) and AR staining at day 21 (C). Images shown were the representatives of five independent experiments. (D) qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression of osteoblast differentiation markers. *p < 0.05, n = 3. Values are shown as mean + SE. (E) TSC1 was effectively deleted in CKO BMSCs and partially deleted in CHet BMSCs as shown by Western blot. (F) Oil red O staining showed enhanced adipogenic differentiation of TSC1-deficient BMSCs, in adipogenic medium for 5 days. (G) The quantitation of Oil red O staining described in F. (H) qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression of adipogenic differentiation markers and transcription factors, in the cultures described in F. *p < 0.05, n = 3. Values are shown as mean + SE. ALP = alkaline phosphatase; AR = Alizarin Red; Runx2 = Runt-related transcription factor 2; Osx = osterix; Alpl = alkaline phosphatase; Bsp = bone sialoprotein protein; ColIa1 = collagen, type I, alpha 1; Ocn = osteocalcin; CTR = control (Tsc1F/F).