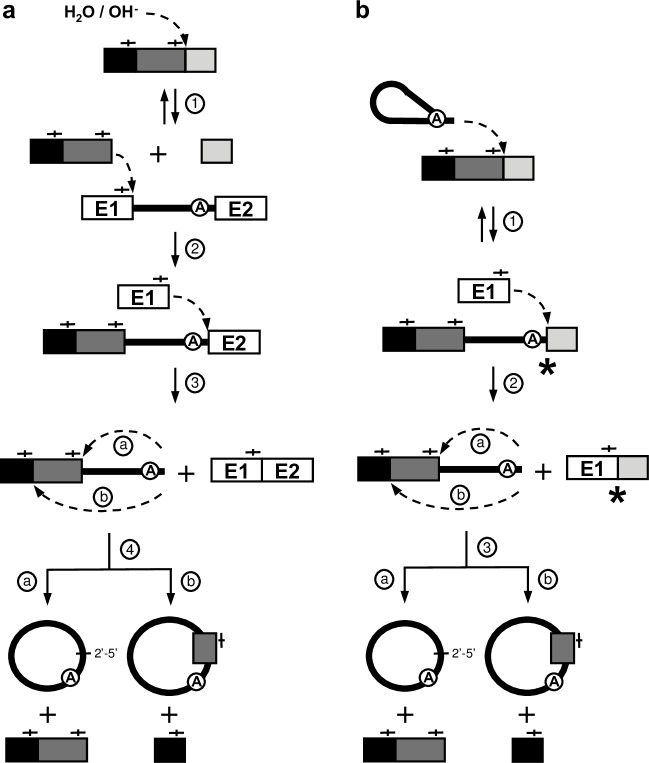
Fig 5. Models for the incorporation of mRNA fragments at the splice junction of intron RNA circles.
(a) External nucleophilic attack pathway [17, 19]. The Ll.LtrB group II intron recognizes, through base pairing interactions, an IBS1/2-like sequence (—|—) on an mRNA and guides the first nucleophilic attack induced by an hydroxyl ion or a water molecule downstream of the recognized sequence (step 1). Next, the 3’-OH of the processed mRNA induces a nucleophilic attack at the exon 1-intron splice junction resulting in its ligation to the 5’ end of the intron and the release of exon 1 (step 2). The 3’-OH of exon 1 is then free to initiate the second transesterification reaction at the intron-exon 2 splice junction, releasing ligated exons and a linear intron harboring a fragment of mRNA at its 5’ end (step 3). The final transesterifictaion reaction is induced at the intron 5’ end (a) or within the mRNA (b) by the 2’-OH of the last nt of the linear intron, just downstream from IBS1/2-like sequences (—|—), resulting in the release of either a head-to-tail circular intron (step 4a) or an intron circle harboring an mRNA fragment at its splice junction (step 4b). (b) Reverse splicing pathway. This pathway is initiated by the reverse splicing of an intron lariat within a non-cognate mRNA downstream of an IBS1/2-like sequence (—|—)(step 1). The 3’-OH of free exon 1 then attacks the phosphodiester bond at the 3’ splice site between the last nt of the intron and the 3’ segment of the mRNA (step 2). This generates a chimeric mRNA consisting of the ltrB-exon 1 (E1) linked to the 3’ segment of the mRNA (E1-mRNA) and a circularization intermediate where the linear intron is still attached to the 5’ segment of the mRNA. The third transesterifictaion reaction is induced at the intron 5’ end (a) or within the mRNA fragment (b) by the 2’-OH of the last residue of the linear intron, just downstream from IBS1/2-like sequences (—|—), resulting in the release of either a head-to-tail circular intron (step 3a) or an intron circle harboring an mRNA fragment at its splice junction (step 3b). The 3’ junction of reverse-spliced introns and the chimeric E1-mRNAs are unique splicing intermediates that distinguish both pathways (asterisks).