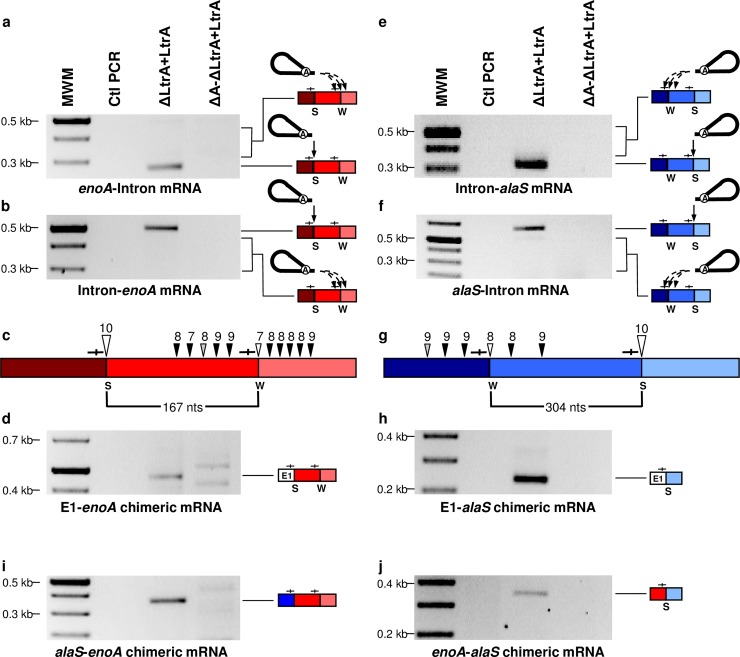
Fig 7. Detection of intermediates unique to the reverse splicing pathway: Ll.LtrB reverse-spliced within L. lactis mRNAs, E1-mRNA and mRNA-mRNA chimeras.
RT-PCR assays were performed to detect the 5’ and 3’ junctions of Ll.LtrB-ΔLtrA+LtrA and Ll.LtrB-ΔA-ΔLtrA+LtrA reverse splicing events within the enoA (red boxes)(a, b) and alaS (blue boxes)(e, f) mRNAs. Complete and dashed arrows indicate reverse splicing of Ll.LtrB lariats within strong (S) and weak (W) IBS1/2-like sequences (—|—) respectively. The strong (S)(10/11 nts)(large arrowhead) and weak (W)(7-9/11 nts)(small arrowhead) IBS1/2-like sequences invaded by reverse splicing are represented (c, g). The sites flanking the mRNA fragments (c, 167 nts and g, 304 nts) initially detected at intron circle splice junctions (Fig 3A) are indicated by open arrowheads. The Ll.LtrB insertion sites were identified in conditions where the enoA or the alaS genes were overexpressed (small open and black arrowheads) or not (large open and small gray arrowheads) from a P23 constitutive promoter. mRNA chimeras between ltrB-exon 1 (E1) and L. lactis mRNAs (d, E1-enoA)(h, E1-alaS) as well as between L. lactis mRNAs (i, alaS-enoA)(j, enoA-alaS) were also detected by RT-PCR at IBS1/2-like sequences.