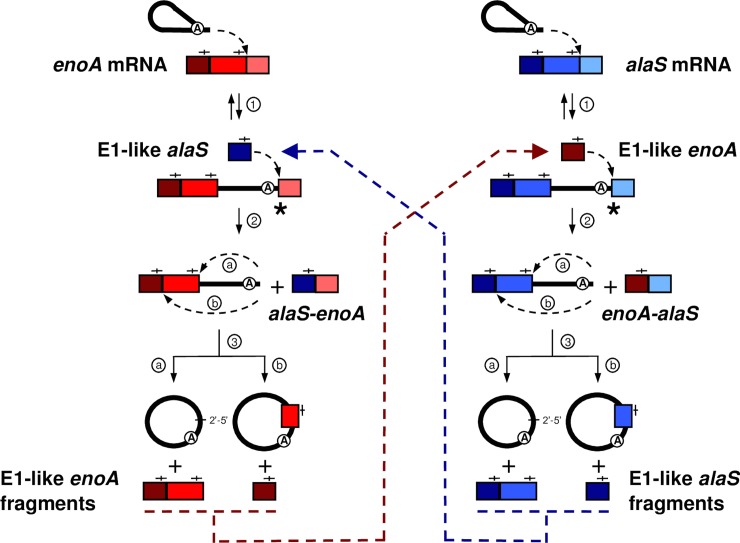
Fig 9. The intergenic group II intron trans-splicing pathway leading to the generation of alaS-enoA and enoA-alaS mRNA chimeras.
Ll.LtrB first recognizes by base pairing and invades by reverse splicing IBS1/2-like sequences on the enoA (red) and alaS (blue) mRNAs (step 1). The 3’OH of intron-processed alaS mRNA fragments (E1-like alaS fragments), harboring IBS1/2-like sequences (—|—) at their 3’ ends (dark blue and blue)(dark blue), can, similarly to free E1, be recruited by the intron to initiate the circularization pathway. These fragments can attack the intron-exon 2 splice junction of the Ll.LtrB-interrupted enoA mRNA (red) leading to the generation of alaS-enoA mRNA chimeras (step 2). Subsequent excision of the intron by circularization releases enoA mRNA fragments (E1-like enoA fragments) with IBS1/2-like sequences at their 3’ ends (step 3a, dark red and red)(step 3b, dark red), which can in turn initiate the generation of enoA-alaS mRNA chimeras with intron-interrupted alaS mRNA (blue).