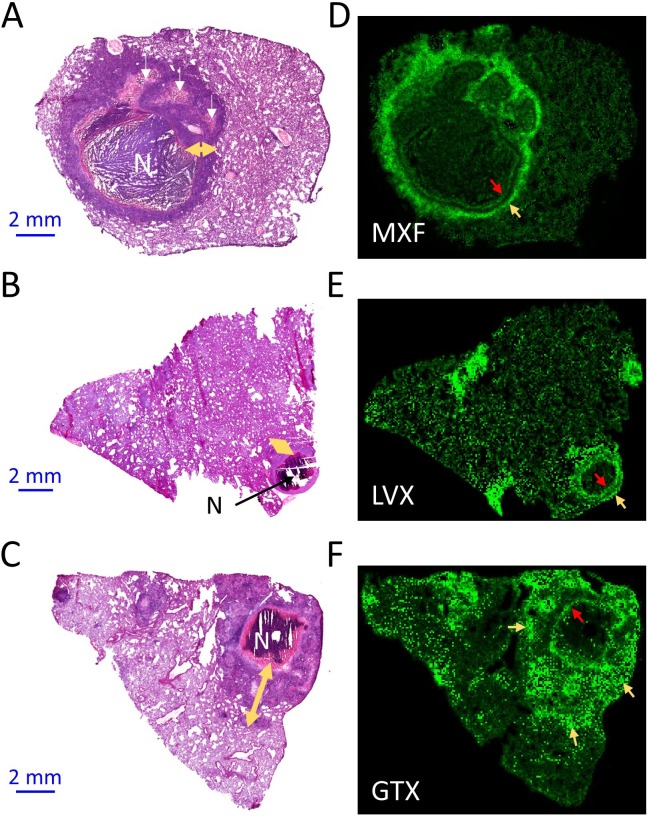
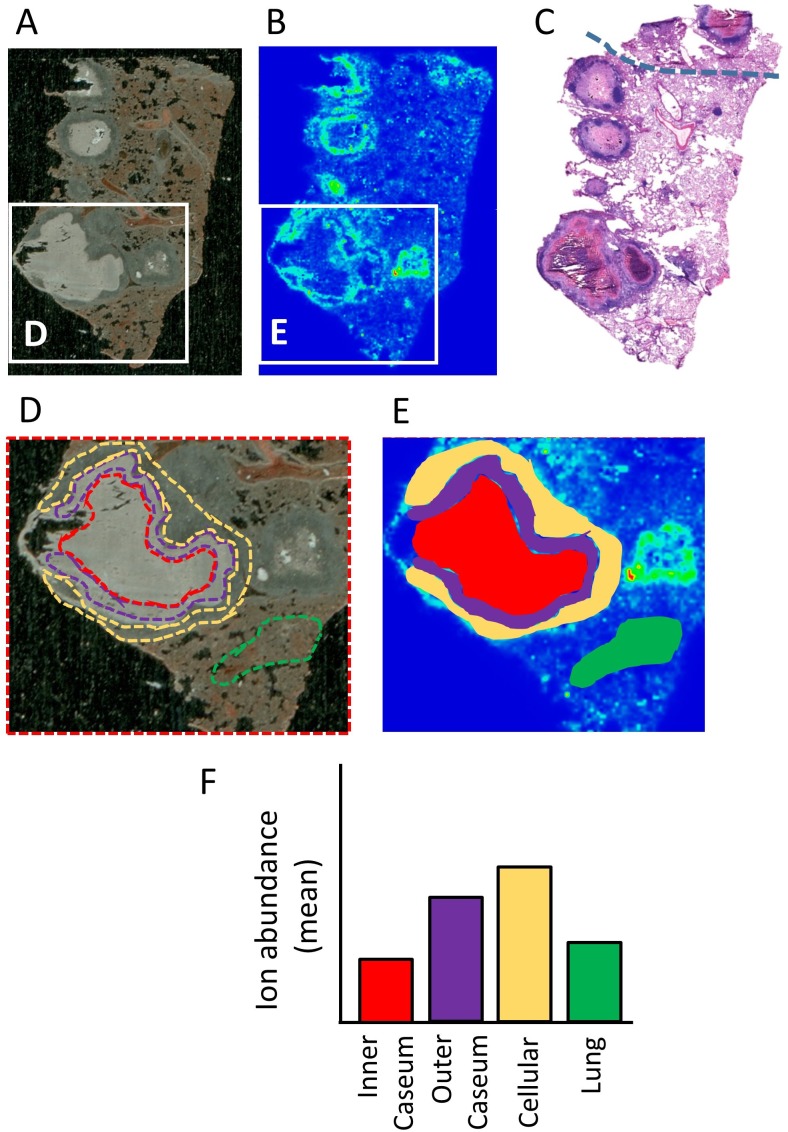
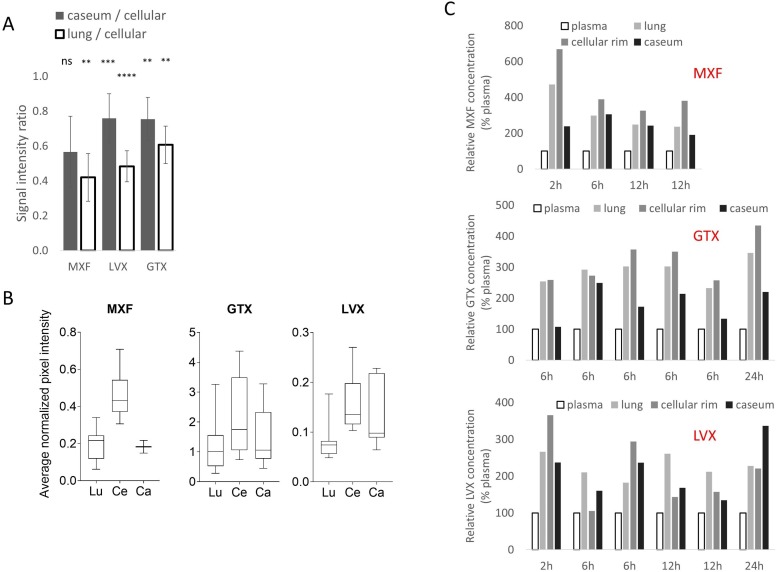
Figure 1. Spatial distribution of fluoroquinolones in infected rabbit lung and lesions.
(a–b–c) Hematoxylin and Eosin (H and E) histology staining of lesions and surrounding lung tissue resected from rabbits that received a single dose of moxifloxacin (MXF) (a), levofloxacin (LVX) (b) or gatifloxacin (GTX) (c). N: necrotic core; white arrows: early caseating foci; yellow double arrows: cellular rim encompassing mostly lymphocytes, macrophages, foamy macrophages, interspersed epithelial cells and neutrophils. Panels d-e-f show the corresponding MALDI-MS ion maps of each drug in a tissue section adjacent to the one stained by H and E. Red arrows highlight the inner drug accumulation ring subtending the caseous core; yellow arrows highlight outer rings or pockets of higher drug abundance further outward from the core.