Figure 2.
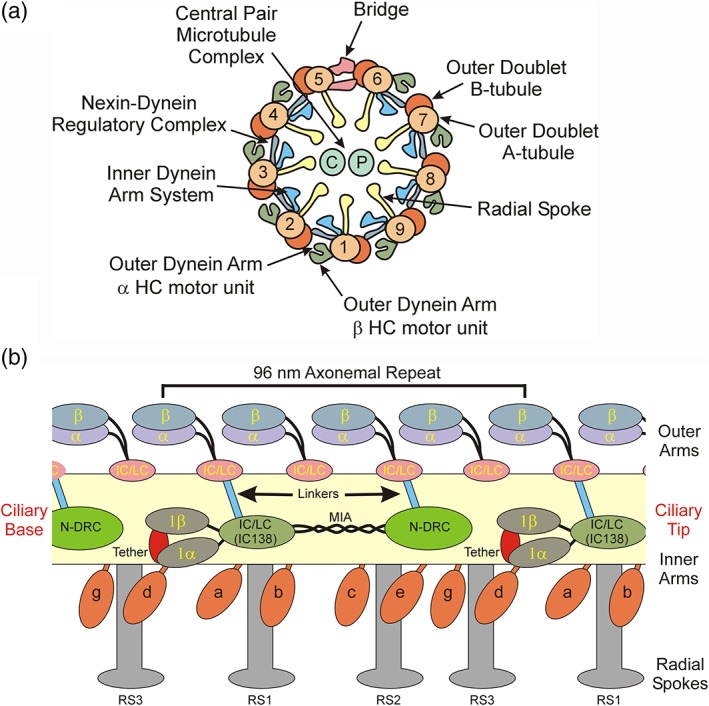
Arrangement and interconnectivity of axonemal motors and regulators. (a) Diagram of the ciliary axonemal cross‐section indicating the key structural elements including the A‐ and B‐tubules of the outer doublet microtubules, the inner and outer dynein arms, nexin‐dynein regulatory complex, radial spokes, central pair microtubule complex, and the bridge structure that spans the gap between doublets 5 and 6. Based on analysis of orthologous components in Chlamydomonas, within the sea urchin outer dynein arm the HCs are arranged with the β HC outermost. (b) diagram illustrating the general arrangement along the axonemal long axis of the inner and outer arm dynein motors and the key regulatory components that control their activity in sea urchin sperm; unlike opisthokonts, in Chlamydomonas the outer arms have three HCs and RS3 is truncated lacking the spoke head and most of the stalk. All these components are tightly associated with A‐tubule (yellow) and the orientation with respect to the ciliary base and tip is indicated. Inner arm I1/f consists of the 1α and 1β HC motors (indicated as 1α and 1β) and the IC/LC complex that contains the key regulator IC138. The motor domains of the I1/f inner arm dynein are attached to the A‐tubule via the tether/tether head complex (red) that restricts their motion. Dyneins transiently interact with the B‐tubule (not shown) in an ATP‐dependent manner to generate force, while the N‐DRC provides a nucleotide‐independent linkage that connects adjacent doublets and acts to resist sliding. This converts the dynein‐generated unidirectional force vector into a microtubule bend. The radial spokes transduce mechanical signals from the central pair microtubule complex (not shown) to the inner arm system. Not shown is the calmodulin spoke complex that interconnects RS2, RS3, and the N‐DRC. Linkers (blue) allow signal transmission from inner arm I1/f and the N‐DRC (green) to the outer arm dyneins. HC, heavy chain; IC, intermediate chain; LC, light chain; N‐DRC, nexin‐dynein regulatory complex [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
