Figure 4.
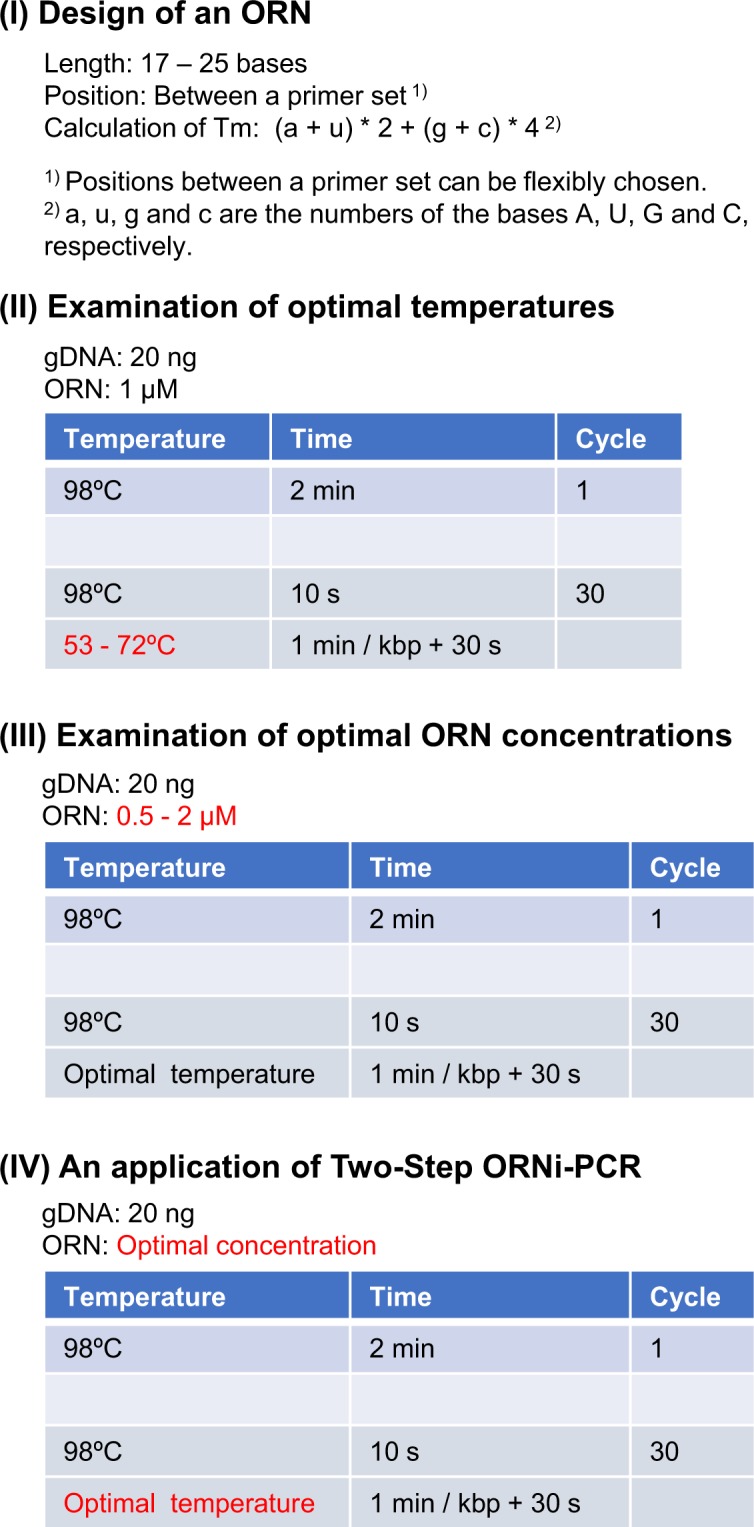
Step-by-step optimisation of Two-Step ORNi-PCR using KOD DNA polymerase. (Step I) Design of an ORN. (Step II) Determination of the optimal temperature. In this step, 1 μM ORN is used as a default. (Step III) Determination of the optimal ORN concentration. (Step IV) Practical application of Two-Step ORNi-PCR, such as detection of nucleotide mutations. Herein, we show an example using gDNA extracted from mammalian cells, for which 20 ng of gDNA and 30 cycles of denaturing and annealing plus elongation were used as a default. Other types of DNA (e.g., plasmids, fragments, cDNA) and α-type DNA polymerases (e.g., Pfu DNA polymerase) can be used for ORNi-PCR. Dependent on materials, the amount of DNA and the number of cycles of denaturing and annealing plus elongation may require modification.
