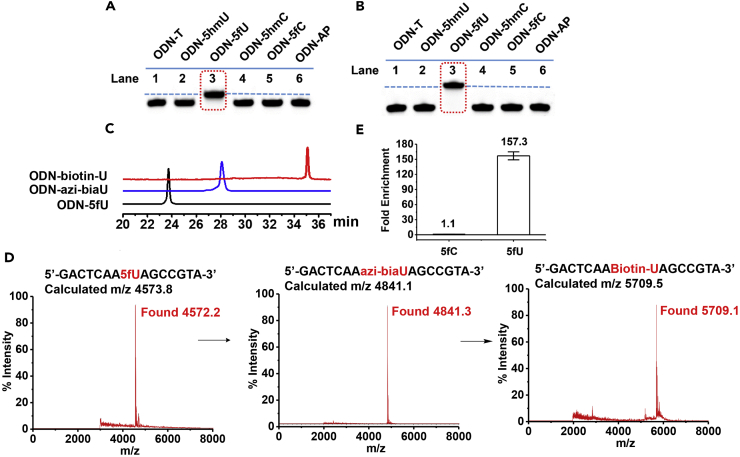
Figure 2.
azi-BIAN Selectively Labels and Enriches 5fU
(A) PAGE analysis of ODN-5fU after incubation with azi-BIAN (lane 3) (dashed line) after being stained with nucleic acid stains (fluorescence mode, λex: 532 nm) when compared with other control DNAs such as ODN-T (lane 1), ODN-5hmU (lane 2), ODN-5hmC (lane 4), ODN-5fC (lane 5), and ODN-AP (lane 6) under the same conditions.
(B) PAGE analysis of ODN-5fU after incubation with azi-BIAN and reaction with DBCO-biotin (lane 3) (dash line) after being stained with nucleic acid stains (fluorescence mode, λex: 532 nm) when compared with other control DNAs such as ODN-T (lane 1), ODN-5hmU (lane 2), ODN-5hmC (lane 4), ODN-5fC (lane 5), and ODN-AP (lane 6) under the same conditions.
(C) RP-HPLC trace (260 nm) of ODN-5fU (black line); ODN-azi-biaU (blue line), which was generated by reaction with azi-BIAN; and ODN-azi-biaU, which was further labeled with DBCO-S-S-PEG3-bitoin (ODN-biotin-U, red line).
(D) MALDI-TOF-spectra of ODN-5fU, ODN-5fU after incubation with azi-BIAN, and ODN-5fU after incubation with azi-BIAN and reaction with DBCO-biotin.
(E) Enrichment tests of a single pool of spike-in amplicons containing 5fU, 5fC, or only canonical nucleobases, using fU-Seq. Values shown are fold enrichment over canonical nucleobases. Data are represented as mean ± SD of biological triplicate.