Figure 1.
FMRP Interacts with Selected Set of C/D Box snoRNAs in Human ESCs and NPCs
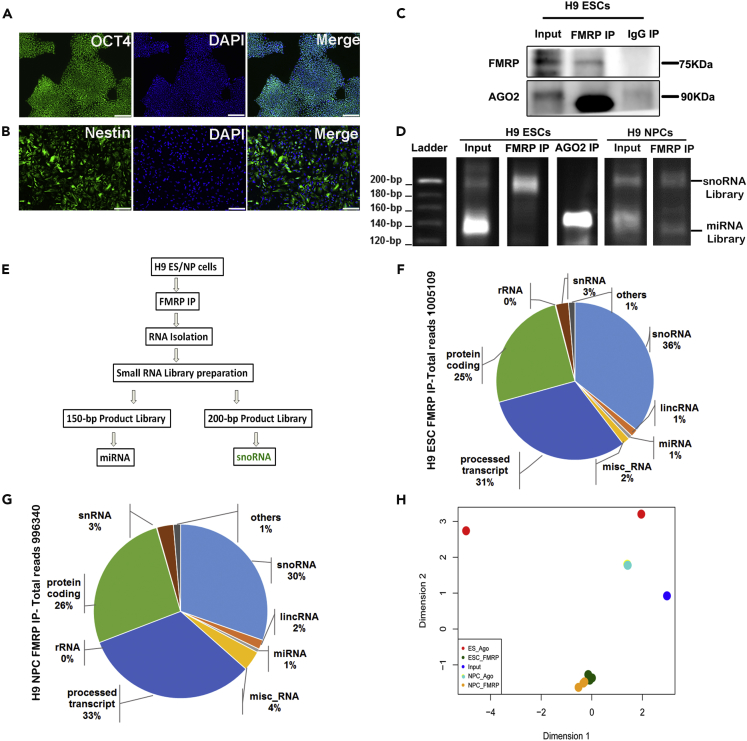
(A) Characterization of H9 hESCs with pluripotency marker OCT4 and nuclear marker DAPI (scale bar, 50 μm).
(B) Characterization of H9 hNPCs with differentiation marker Nestin and nuclear marker DAPI (scale bar, 50 μm).
(C) Immunoblot for FMRP and AGO2 from H9 hESC lysate after FMRP and IgG immunoprecipitation.
(D) Polyacrylamide gels showing mobility of cDNA libraries prepared from RNA extracted after immunoprecipitation with FMRP and AGO2 from H9 hESC and hNPC lysate.
(E) Schematic showing the experimental workflow to identify FMRP-associated small RNAs.
(F) Pie chart showing the distribution of different classes of small RNAs from the sequence obtained from the 200-bp band of the library from H9 hESCs, n = 3.
(G) Pie chart showing the distribution of different classes of small RNAs from the sequence obtained from the 200-bp band of the library from H9 hNPCs, n = 3.
(H) Principal component analysis (PCA) chart indicating clustering of snoRNA libraries in H9 hESCs and H9 hNPCs, hESC FMRP IP n = 3, hNPC FMRP IP n = 3, hESC Input n = 1, and hESC AGO2 IP n = 2.