FIGURE 1.
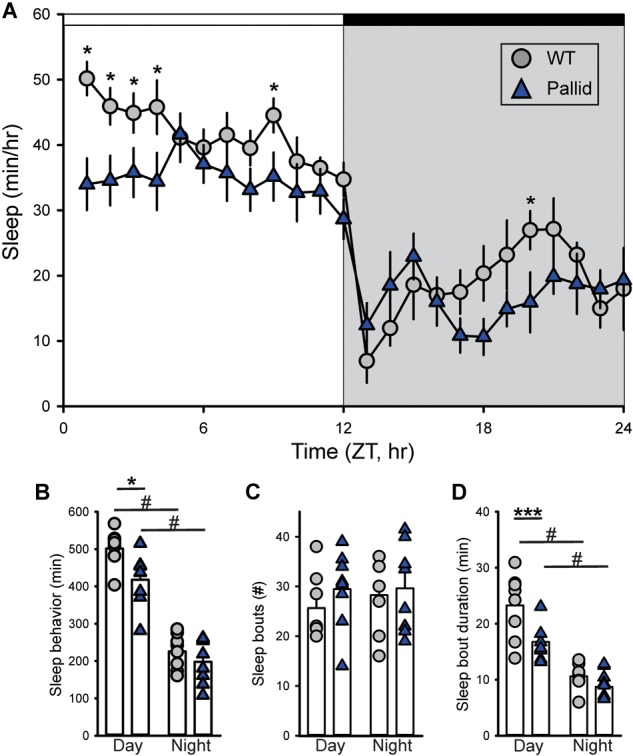
Altered timing of sleep behaviour in BLOC-1-deficient pallid mice. Video recording in combination with automated mouse tracking analysis software was used to measure immobility-defined sleep. (A) The temporal patterning of immobility-defined sleep was altered in the pallid mice, with their amount of sleep reduced in the early day. Running averages (1 h bin) of immobility-defined sleep in wild-type (WT) and pallid mice are plotted. ZT, Zeitgeber Time. 24-h profiles of sleep behaviour were analysed using a two-way ANOVA (Table 1) with genotype and time as factors, followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, ∗P < 0.05. Data points are the mean ± SEM, n = 8 animals/genotype. (B) Pallid mice slept significantly less than WT during the day. (C) The number of sleep bouts was unaltered in mutant mice. (D) The duration of sleep in each bout was reduced for pallid mice in the day-time. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM and were analysed using the Student’s t-test to compare the results obtained between genotypes (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001) or within the genotype (#P < 0.05).
