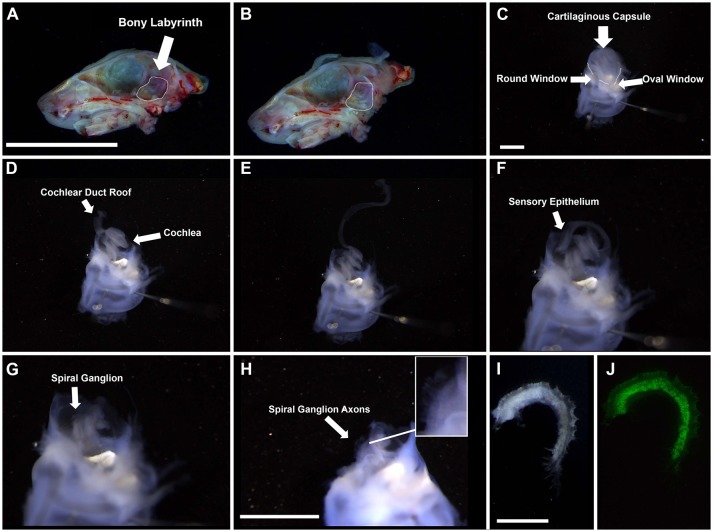
Figure 1.
Gross dissection of the spiral ganglion. (A,B) Interior view of the neonatal skull after heads were split along the midline and the brain was removed. Dotted line highlights the bony labyrinth within the temporal bone of the right hemisphere. Scale bar; 10 mm (C) Appearance of the harvested bony labyrinth after removal of extraneous tissue. Top half contains the cartilaginous capsule surrounding the cochlea. Bottom half contains the semicircular canals of the vestibular system. Scale bar; 1 mm (D–F) Removal of cochlear duct roof and sensory epithelium from the modiolus. (G,H) Appearance of the spiral ganglion. Axons projecting from the spiral ganglion neurons are visible (see inset). Scale bar; 1 mm (I,J) Magnified portion of the spiral ganglion after removal from the modiolus. I, bright field. J, Tau-EGFP. Scale bar; 100 μm.