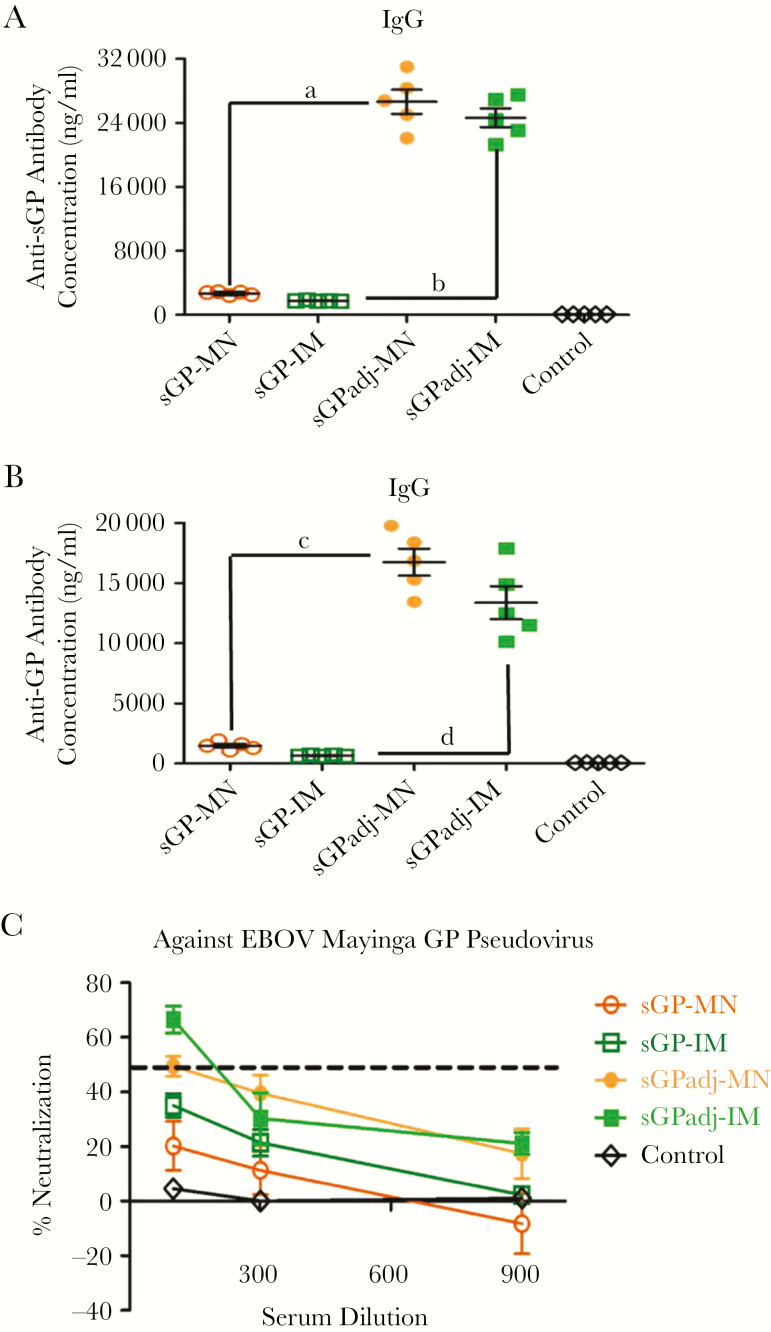
Figure 3.
Analysis of antibody responses induced by microneedle (MN) patch or intramuscular (IM) delivery of soluble glycoprotein (sGP) with or without Matrix-M adjuvant. Mice (groups of 5) were vaccinated twice at 4-week intervals by MN patch delivery (sGPadj-MN) or IM injection (sGPadj-IM) of sGP in formulation with Matrix-M or by MN patch delivery (sGP-MN) or IM injection (sGP-IM) of the same amount (5 µg) unadjuvanted sGP. The control group received IM injection of 50 µL phosphate-buffered saline. Serum samples were collected at 2 weeks after the second immunization. (A) The levels of sGP-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using purified sGP as coating antigen. (B) The levels of GP-specific IgG antibodies were determined by ELISA using purified GP as coating antigen. The antibody concentration was determined from a standard curve and expressed as ng/ml. Statistical analysis for differences in antibody responses against sGP and GP between indicated groups (denoted by “a” through “d”) were done by a a 2-tailed unpaired t test. a, sGPadj-MN vs sGP-MN (against sGP), P = .0001; b, sGPadj-IM vs sGP-IM (against sGP), P = .0001; c, sGPadj-MN vs sGP-MN (against GP), P = .0001; d, sGPadj-IM vs sGP-IM (against GP), P = .0001. (C) Neutralizing activity of sera was determined by incubating 500 plaque-forming units of Mayinga Ebola virus GP pseudoviruses with serial 3-fold dilutions of serum samples from each vaccinated mouse. Neutralization was measured as percentage decrease in luciferase expression compared with virus-naive mouse sera controls.