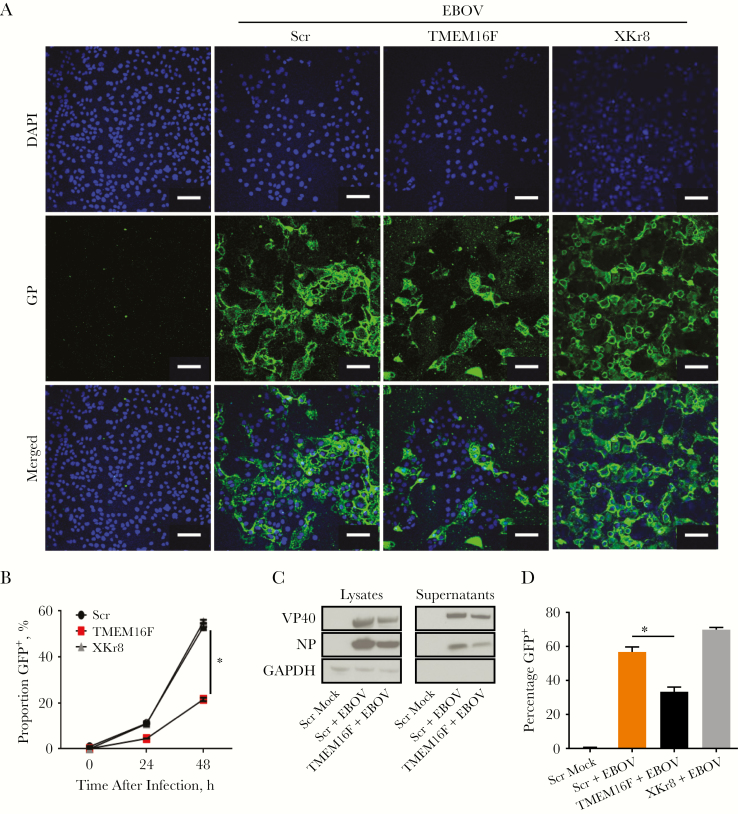
Figure 2.
Blocking transmembrane protein 16F (TMEM16F) function reduces the levels of viral membrane-associated PtdSer leading to decreased infectivity. A, Huh7/short hairpin (sh)Scramble, Huh7/shTMEM16F and XK-related protein 8 (XKr8) cell lines were mock infected or infected with Ebola virus (EBOV) at a multiplicity of infection (of 0.3 plaque-forming unit /cell for 48 hours. Cells were stained for EBOV glycoprotein (GP) to determine the relative number of infected cells. (Scale bar represents 40 μm). B, Cells were infected with EBOV expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) and analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the relative percentages of infected (GFP+) cells at 24 and 48 hours. C, Amount of viral proteins in lysates and supernatants determined at 48 hours in Huh7/shScramble or Huh7/shTMEM16F shRNA cell lines. D, Supernatants from Huh7/shScramble and Huh7/ shTMEM16F cells were added to Vero E6 cells for 20 hours to determine the relative production of infectious virus. Means shown in graphs are from triplicate samples, with standard deviations and are representative of 3 independent experiments, *P < .001 (Student t test). Abbreviations: DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Scr, scrambled shRNA.