Figure 1.
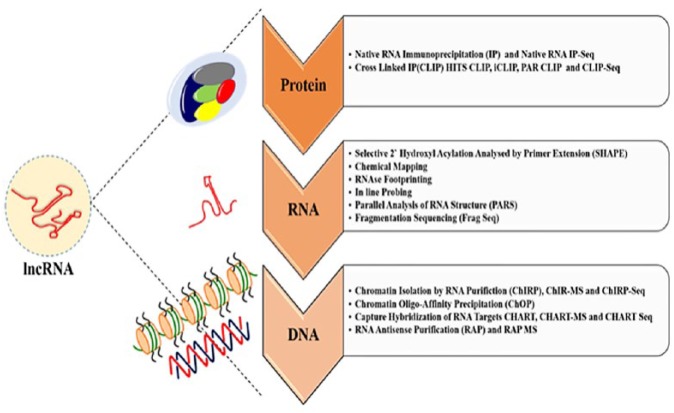
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNAs) interactome and strategies. The lncRNA interactome is complex and involves DNA, RNA, and/or proteins. It is important to understand the mechanisms and functions of lncRNAs and the role they play in normal and diseased states. The methods or strategies employed for studying lncRNAs can be achieved by either of the following techniques. Protein-lncRNA interactions broadly represent the protein partners of lncRNAs and suggest their functional mechanisms and pathways. RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and crosslinked immunoprecipitation (CLIP) techniques provide clues of the associated RNAs when ribonucleoprotein complexes are pulled down based on the antibody of interest. The coupling of these techniques with high-throughput RNA sequencing and mass spectrometry could help identify the protein interactions to lncRNAs genome-wide or simply other proteins associated in the RNA binding protein complex or the protein of interest, respectively. Techniques that shed information based on the structural features like the secondary and tertiary structure of the lncRNAs eventually aid toward understanding the lncRNA function. The structural features can be harnessed through techniques and chemical reagents that cleave RNA at specific nucleotides or attack the regions that are exposed to the solvent, avoiding the RNA regions that are buried inside or are covered by proteins. Crosslinking also could reveal the intramolecular interactions that could be extended over a long range. Ribonucleases with different cleavage specificities can be used to obtain a RNAse footprint of potential regions covered by the proteins. Methods such as selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE) and in-line probing aim at providing information on the local nucleotide flexibility. Coupling of SHAPE with sequencing could provide details of binding regions. Fragment sequencing (FragSeq) and parallel analysis of RNA structure (PARS), on the other hand, also employ RNase digestion to provide information on the RNA structure. Several techniques have been developed to identify the genomic DNA targets of lncRNAs. Based on the workflow backbone of chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), chromatin isolation by RNA purification (ChIRP) helps identify lncRNAs associated with unique chromatin marks, whereas techniques such as chromatin oligo-affinity purification (ChOP) and capture hybridization of RNA targets (CHART) are basically used to identify the complementary DNA regions that interact with the RNA of interest. In addition, coupling with RNA sequencing, quantitative PCRs and mass spectrometry could yield important information regarding the RNA and protein interactome, respectively.