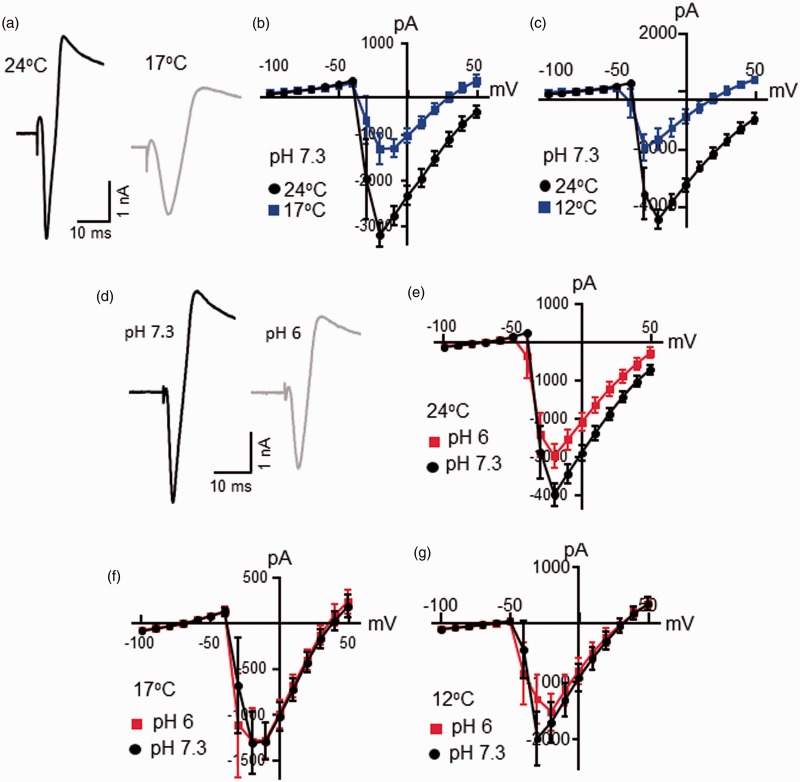
Figure 3.
Effects of cooling temperatures and low pH on voltage-activated inward currents in nociceptive-like trigeminal ganglion neurons. (a) Sample traces of voltage-activated inward currents in a nociceptive-like TG neuron at 24°C (black) and 17°C (gray). The voltage step was from −100 mV to 50 mV. (b) I-V curve of voltage-activated inward currents of nociceptive-like TG neurons at 24°C (black, n = 6) and 17°C (blue, n = 6). (c) I-V curve of voltage-activated inward currents of nociceptive-like TG neurons at 24°C (black, n = 10) and 12°C (blue, n = 10). In (a) to (c), the Krebs bath solution for cell perfusion had pH of 7.3. (d) Sample traces of voltage-activated inward currents in a nociceptive-like TG neuron at pH 7.3 (black) and pH 6 (gray). The voltage step was from −100 mV to 50 mV. (e) I-V curve of voltage-activated inward currents of nociceptive-like TG neurons at pH 7.3 (black, n = 15) and pH 6 (red, n = 15). In both (d) and (e), the Krebs bath solution was maintained at 24°C. (f) I-V curve of voltage-activated inward currents of nociceptive-like TG neurons at pH 7.3 (closed bar, n = 6) and pH 6 (open bar, n = 6). The Krebs bath solution was maintained at 17°C. (g) I-V curve of voltage-activated inward currents of nociceptive-like TG neurons at pH 7.3 (closed bar, n = 10) and pH 6 (open bar, n = 10). The Krebs bath solution was maintained at 12°C. Data represent mean ± SEM.