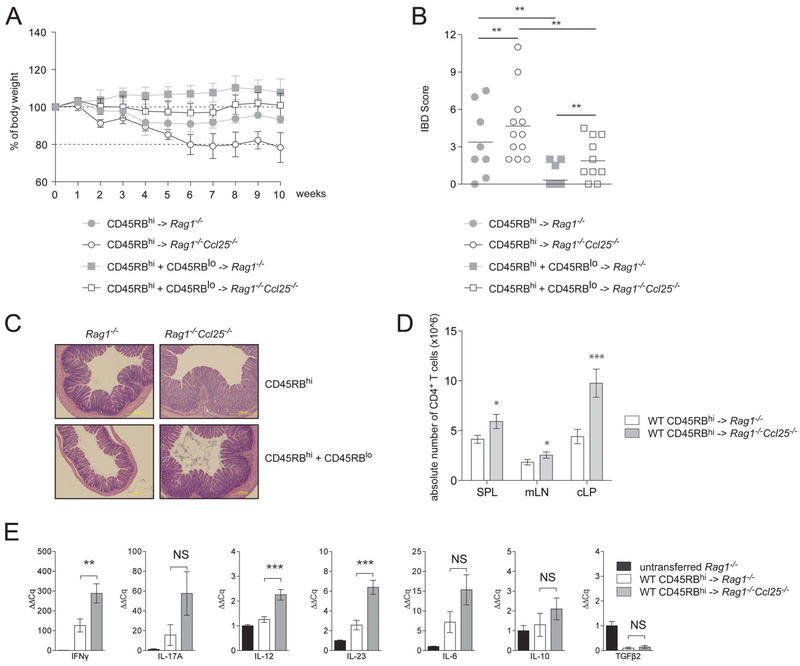
FIGURE 3.
Rag1−/−Ccl25−/− mice display exacerbated T cell-mediated chronic colitis. A, Sex- and aged-matched Rag1−/− and Rag1−/−Ccl25−/− mice were adoptively transferred with WT CD45RBhi or CD45RBhi and CD45RBlo CD4+ T cells to respectively induce or protect from experimental T cell-mediated colitis. Mice were monitored weekly and weight loss was reported and expressed as the percentage of initial body weight (mean ± SD). Data representative of 5 pooled experiments. B, Comparison of IBD scores obtained by H&E histological examination of paraffin-embedded sections from distal colons. Rag1−/− recipient mice are depicted in filled gray circles (after CD45RBhi transfer) or filled gray squares (after CD45RBhi and CD45RBlo cotransfers), and Rag1−/−Ccl25−/− mice are depicted in open circles (after CD45RBhi transfer) or open squares (after CD45RBhi and CD45RBlo cotransfers). C, Representative H&E staining of Rag1−/− and Rag1−/−Ccl25−/− recipient mice after transfer of CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells or after cotransfer of CD45RBhi and CD45RBlo CD4+ T cells (10× magnification). D, Absolute CD4+ T-cell numbers among leukocytes quantified by flow cytometry in Rag1−/− and Rag1−/−Ccl25−/− SPL, mLN, and cLP after CD45RBhi CD4+ T cell transfer (mean ± SD). Data are representative of 5 pooled experiments. E, The qPCR mRNA profiling in Rag1−/− and Rag1−/−Ccl25−/− colons after transfer of WT CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells. Normalization was performed to HPRT and untransferred Rag1−/− control mice. Data represent of 1 of 5 experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005; NS, not significant.