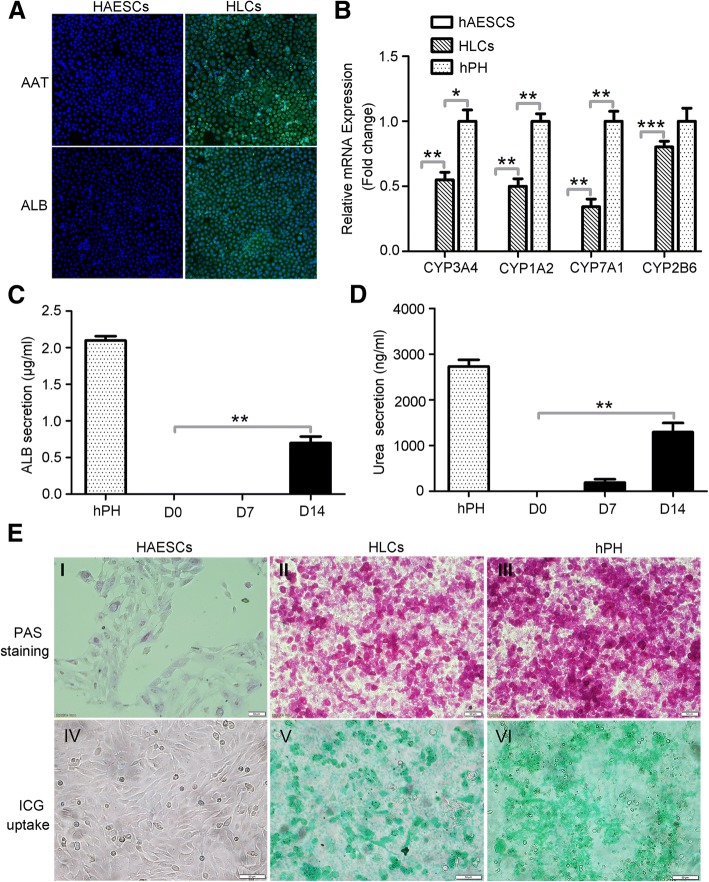
Fig. 4.
Functional analysis of HLCs derived from hAESCs. a Immunofluorescence analysis of AAT and ALB in hAESCs and HLCs. There were no expressions of AAT and ALB in hAESCs, and the HLCs specifically expressed both AAT and ALB after induction of 14 days. b Expressions of hepatocyte-specific markers. The mRNA expressions of CYP3A4, CYP1A2, CYP7A1, and CYP2B6 were detected by RT-qPCR in hAESCs, HLCs, and hPH, and the results showed that HLCs specifically expressed all of these markers. c Secretion of albumin. The secretion of albumin was determined by ELISA in the culture medium of hPH, hAESCs, and HLCs, and the results showed that the HLCs specifically secreted albumin after induction of 14 days. The hPH cells were used as the positive control. d Biochemical analysis of urea. The urea production was also secreted in culture medium of HLCs after induction of 7 and 14 days. The hPH cells were used as the positive control. e PAS staining and ICG uptake. The glycogen storage and ICG uptake function of hAESCs, HLCs, and hPH were analyzed by PAS staining (I, II, III) and ICG uptake (IV, V, VI), respectively, and the results showed that HLCs can be specifically stained by PAS and uptaken ICG. Significance was measured via a two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, *P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001