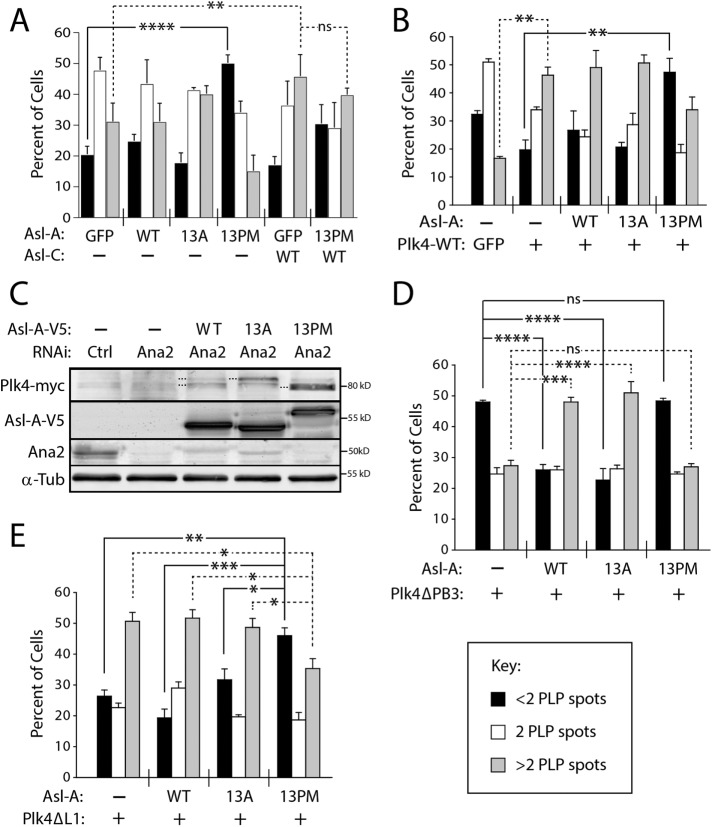
FIGURE 5:
Asl-A phosphomutants control kinase activity by manipulating Plk4 autoinhibition. (A) Asl-A-13PM expression causes centriole loss. The indicated Asl-GFP constructs were transfected into S2 cells and then induced the next day to express for 72 h. Cells were immunostained for PLP to mark centrioles. Significant centriole loss (less than two centrioles) occurs in cells expressing Asl-A-13PM. In contrast, centrioles are amplified (more than two centrioles) in cells expressing Asl-C, and centrioles are similarly amplified in cells coexpressing Asl-C and Asl-A-13PM. n = 3 experiments per construct (total 300 cells/construct). (B) Coexpressed Asl-A-13PM not only blocks the centriole amplification induced by Plk4 expression but causes significant centriole loss. Plk4-GFP/Asl-A-V5 dual-gene expression plasmids were transfected into S2 cells, and then were induced the next day to express for 72 h. Cells were immunostained for PLP to mark centrioles, and centriole numbers measured. n = 3 experiments per construct (total 300 cells/construct). (C) Regulation of Plk4 by Asl-A mutants occurs independently of Ana2. S2 cells were codepleted of endogenous Asl and Ana2 for 7 d. On day 5, Plk4-GFP and the indicated Asl-A-V5 constructs were cotransfected into cells and expression was induced the next day. Immunoblots of cell lysates were probed for Ana2, GFP, V5, and α-tubulin. (D) Asl-A-WT and Asl-A-13A can activate an autoinhibited Plk4-ΔPB3 mutant. S2 cells were transfected with Plk4-ΔPB3-GFP/Asl-A-V5 dual-gene expression plasmids, and samples were prepared as in B. n = 3 experiments per construct (total 300 cells/construct). (E) A Plk4 mutant incapable of autoinhibition is inhibited by Asl-A-13PM. S2 cells were transfected with Plk4-ΔL1-GFP/Asl-A-V5 dual-gene expression plasmids, and samples were prepared as in B. n = 3 experiments per construct (total 300 cells/construct).