FIGURE 5:
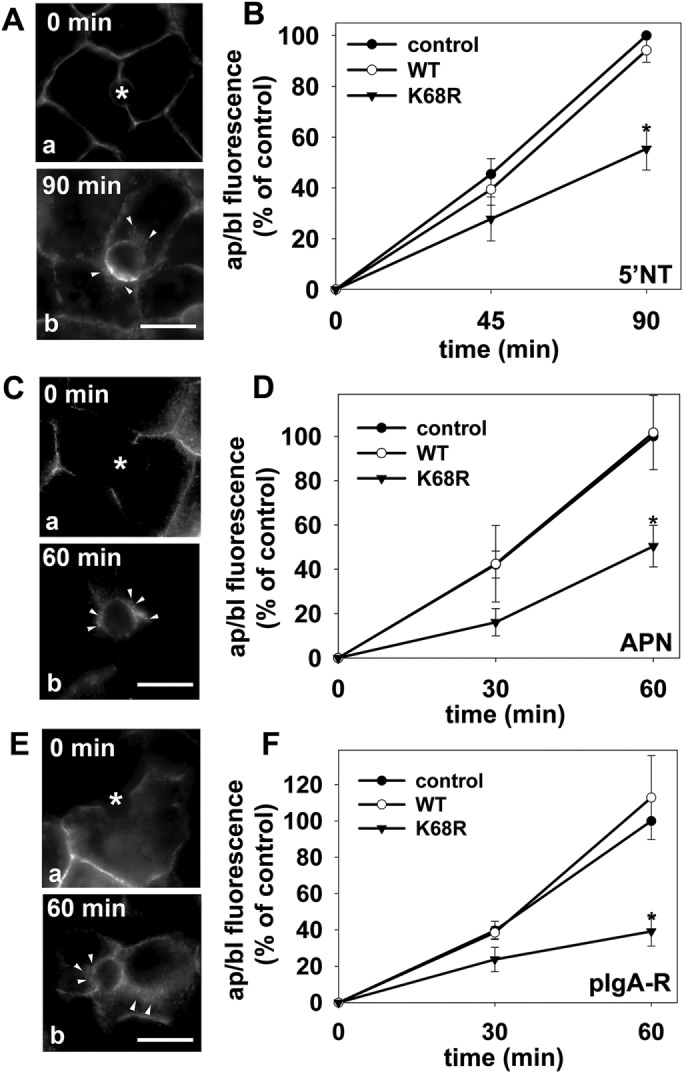
Transcytosis is impaired to a similar extent for different classes of apical proteins in cells expressing sumo-deficient/K68R rab17. (A–F) Control (uninfected) cells and cells expressing wild-type or sumo-deficient/K68R rab17 were basolaterally labeled with antibodies specific for the extracellular epitopes of the indicated apical proteins at 4°C. Cells were additionally infected with recombinant adenoviruses expressing pIgA-R in E and F. After excess antibodies were washed away, antibody–antigen complexes were chased for 0, 60 min, or 90 min as indicated (A, C, and E) at 37°C. Cells were fixed, permeabilized and labeled with secondary antibodies to detect transcytosed APN (A), 5′NT (C) or pIgA-R (E). Asterisks are marking unlabeled canaliculi. Images are representative of at least three experiments. Bar = 10 μm. (B, D, F) Control (uninfected) WIF-B cells or cells expressing wild-type or sumo-deficient/K68R rab17 were basolaterally labeled for the indicated apical proteins as described in Figure 1 and chased for 0, 45, or 90 min (B) or 0, 30 or 60 min (D and F) at 37°C. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with secondary antibodies to detect the transcytosed proteins. Random fields were visualized by indirect immunofluorescence. From micrographs, the average pixel intensity of each marker at selected regions of interest placed at the apical or basolateral membrane of the same WIF-B cell was measured. The averaged background pixel intensity was subtracted from each value, and the ratio of apical (ap) to basolateral (bl) fluorescence intensity was determined. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM for 5′NT (B), APN (D), and pIgA-R (F). Measurements were performed on at least three independent experiments. *p ≤ 0.05.
